Evolutionary Biologist Builds AirSlate Into Fast-Growing Document Workflow Business – Forbes
The global document workflow management software market is a big and growing business, reaching $8.52 billion in 2021 and estimated to grow to $55.35 billion in 2028, according to Grandview Research.
One company, airSlate, disrupted the category by focusing on the needs of individual users at small and mid-sized businesses and using the scientific method to constantly test and learn its way to product development, customer satisfaction and market share growth.
Headquartered in Boston, airSlate began life as PDFFiller in 2008, a company founded by Vadim Yasinovsky, who developed a way to create editable forms and documents from PDF files. That company struggled to grow until Yasinovsky’s friend Borya Shakhnovich became CEO and broadened the company into document workflow and digital transformation that turned the company into a fast-growth software business. This founder’s journey story is based on my interview with Shakhnovich.
airSlate Co-Founder and CEO Borya Shakhnovich.
Prior to airSlate, Shakhnovich was the founder of Orwik, a community network for scientists and institutions, and Yasinovsky was one of his investors. “I came to one of my investors who was running PDFFiller at the time. And I said, ‘Look, I have this marketing technology, why don’t you apply it To PDFFiller?’ And he said, ‘I don’t know anything about how to apply this marketing technology, why don’t you come and build it with me.’ And that’s how airSlate was really born,” says Shakhnovich.
At that time, PDFFiller was a small company with $400,000 in annual revenue. Using Shakhnovich’s technology and business savvy, the team bootstrapped PDFFiller to grow to reach 160,000 customers, 160 employees and $60 million annual revenue. After several years, Shakhnovich moved into the CEO role and the company greatly expanded its product offering and formally became airSlate in 2018.
Today the company positions itself as a global SaaS technology company that provides no-code business process automation and document management solutions to companies of all sizes. Its PDF editing, e-signature workflow, and business process automation solutions allow users to solve document workflow challenges more easily and at lower cost than other enterprise software providers, according to Shakhnovich.
The company continues to experience significant growth, increasing revenue 50% year over year, expanding its customer base and including partner collaborations with Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS), Microsoft, Samsung, SoftwareOne, Xerox and others. “Right now, we have over one million customers and about 1,000 employees,” says Shakhnovich.
As a result, the company has raised a total of $181.5 million in venture funding to date. Its most recent $51.5 million financing on June 16, 2022 led by G Squared, including a strategic partnership with UiPath, valued airSlate at $1.25 billion. Additional investors include Silicon Valley Bank, Morgan Stanley Expansion Capital, High Sage Ventures, General Catalyst, Horizon Capital and others. “We’ve run this business pretty much cashflow neutral throughout the last 10 years. So all of the money that we raised is either on the balance sheet or used for M&A,” says Shakhnovich.
Before becoming an entrepreneur, Shakhnovich was an evolutionary biologist and approaches business with an evolutionary design model and attributes his success as a leader is to his academic training. “I like interdisciplinary approaches to solving complex problems whether using Physics to understand customer acquisition or using Biology to understand customer retention. Before my life in startups and online marketing, I used to teach bioinformatics at BU and do systems biology research at Harvard,” says Shakhnovich.
Shakhnovich grew up in Russia up until the age of eleven. His family moved to the U.S. in 1990 when his father became a professor of chemistry at Harvard. Shakhnovich followed in his father’s footstep and pursued an academic career. He attended the University of Illinois, in Urbana Champaign. “I studied computational biophysics, so nothing that’s even remotely related to business,” says Shakhnovich. After graduating, he went on to earn his PhD at Boston University in bioinformatics, which is the statistical analysis of biological systems, including genes, proteins and evolution. He then became a professor of Bioinformatics at Boston University in 2004 and soon thereafter moved over to Harvard in 2006 to lead a Systems Biology group there.
In 2008, right before the beginning of the financial crisis, he left Harvard to start his own business. “I always wanted to be an entrepreneur. I always wanted to create my own business. And in a lot of ways, being an academic is actually like running your own very small business,” says Shakhnovich.
He founded Orwik a professional network for researchers that was meant to solve the problem of transparency in the academic process, but after four years trying to make it work, the business never took off. “I made all of the mistakes that I think beginning entrepreneurs make. I started building a company for myself instead of for customers and built a product without testing it in the marketplace,” says Shakhnovich. He apparently learned his lesson well with the creation and exponential growth of airSlate.
As for the future? “Over the next five to ten years, we would like to train a million people on using our technology to increase their efficiency and value to their own business. We want to help an employee that was earning $40,000 to $50,000 and turn them into an employee that is critical to the business, earning $100,000 to $120,000. And that’s the mission of the company overall,” concludes Shakhnovich.
- Published in Uncategorized
Top data modeling tools of 2022 – TechRepublic
Register for your free TechRepublic membership or if you are already a member, sign in using your preferred method below.
We recently updated our Terms and Conditions for TechRepublic Premium. By clicking continue, you agree to these updated terms.
Invalid email/username and password combination supplied.
An email has been sent to you with instructions on how to reset your password.
By registering, you agree to the Terms of Use and acknowledge the data practices outlined in the Privacy Policy.
You will also receive a complimentary subscription to TechRepublic’s News and Special Offers newsletter and the Top Story of the Day newsletter. You may unsubscribe from these newsletters at any time.
All fields are required. Username must be unique. Password must be a minimum of 6 characters and have any 3 of the 4 items: a number (0 through 9), a special character (such as !, $, #, %), an uppercase character (A through Z) or a lowercase (a through z) character (no spaces).
Top data modeling tools of 2022
Your email has been sent
Identify which data modeling tools are right for your business. Discover the top tools of 2022 now.
Data modeling tools play an important role in business, representing how data flows through an organization. It’s important for businesses to understand what the best data modeling tools are across the market as well as for their specific operational needs. In this guide, TechRepublic has reviewed the top data modeling tools, discussing the pros and cons and differentiating features of each solution.
Jump to:
Data modeling is the process of creating and using a data model to represent and store data. A data model is a representation — in diagrammatic or tabular form — of the entities that are involved in some aspect of an application, the relationships between those entities and their attributes.
SEE: Job description: Big data modeler (TechRepublic Premium)
Data models represent many aspects of an organization’s operations: business processes, informational needs, data required to support processes, organizational structure and systems architecture.
These models can be either conceptual, logical or physical. A good data model includes primary and foreign keys, which allow you to maintain referential integrity; this allows your database to grow without data loss. You also need design patterns like aggregate tables, lookup tables and transactional tables, all of which help to organize your data depending on its usage.
Data modeling tools are software solutions that help analysts make sense of large amounts of complex data, turning them into visual representations such as graphs, charts and diagrams. These are some of the top data modeling options on the market today:
IDERA ER/Studio is a data modeling software suite for business analysts, architects and developers. It allows them to create data models for various applications and provides several components such as business data objects, shapes, text blocks and data dictionary tables. IDERA ER/Studio is an intuitive tool that is capable of easily integrating different enterprise systems, giving users full control over their data management process.
erwin Data Modeler by Quest is a cloud-based enterprise data modeling tool for finding, visualizing, designing, deploying and standardizing enterprise data assets. It provides logical and physical modeling and schema engineering features to assist with the modeling process.
erwin is a complete solution for modeling complex data and has an easy drag-and-drop interface for creating and modifying structures, tables and relationships. In addition, this tool provides centralized management dashboards for administrators to view conceptual, logical and physical models.
IBM InfoSphere Data Architect is a data modeling tool that supports business intelligence, analytics, master data management and service-oriented architecture initiatives. This tool allows users to align processes, services, applications and data architectures. Data modeling, transformation, DDL script generation, database object creation, debugging, management and SQL stored procedures and functions are all available within IBM InfoSphere Data Architect’s portfolio of features.
Moon Modeler is a data modeling solution for visualizing MongoDB and Mongoose ODM objects. It also supports MariaDB, PostgreSQL and GraphQL. This tool allows users to draw diagrams, reverse engineer, create reports and generate scripts to map object types to the appropriate databases in the right format.
DbSchema Pro is an all-in-one database modeling solution that allows you to easily design, visualize and maintain your databases. It has many features to help you manage and optimize your data, including a graphical query builder, schema comparer, schema documentation, schema synchronization and data explorer. It can be used with many relational and NoSQL databases like MongoDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server and MariaDB.
Oracle SQL Developer Data Modeler is a free graphical tool that enables users to create data models with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface. It can create, browse and edit logical, relational, physical, multi-dimensional and data-type models. As a result, the software streamlines the data modeling development process and improves collaboration between data architects, database administrators, application developers and end users.
Archi (Archimate modeling is an open-source solution for analyzing, describing and visualizing architecture within and across various industries. It’s hosted by The Open Group and aligns with TOGAF. The tool is designed for enterprise architects, modelers and associated stakeholders to promote the development of an information model that can be used to describe the current or future state of an organization’s environment.
MagicDraw is a business process, architecture, software and system modeling tool that enables all aspects of model building. It provides a rich set of graphical notations to model data in all its complexities, from entities to tables. Its intuitive interface provides wizards for the most common types of models, including Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERD), Business Process Models and Notation (BPMN), and Object-Oriented Design Models (OO). In addition, MagicDraw supports round-trip engineering with Unified Modeling Language (UML).
Lucidchart is an intuitive and intelligent diagramming application that makes it easy to make professional-looking flowcharts, org charts, wireframes, UML diagrams and conceptual drawings. This tool allows administrators to visualize their team’s processes, systems and organizational structure. It also enables developers to create UI mockups in a few clicks.
It has a drag-and-drop interface which simplifies the process of creating these diagrams. It also integrates with other business applications like Google Drive, Jira and Slack, which helps users to complete project work faster.
ConceptDraw is a diagramming solution that enables users to create diagrams or download and use premade ones. The data modeling tools include: ‘Table Designer,’ ‘Database Diagrams’ and ‘Data Flow Diagram.’ Users can also create flowcharts, UML diagrams, ERD diagrams, mind maps and process charts with this solution.
The best data modeling tools allow you to represent information through tables, schemas, logical diagrams and entity relationship diagrams. These tools also have query-building and validation rules that allow you to validate the design before deploying it live. Key features to look out for include:
Data modeling is often done as part of a larger cycle, which includes development or change management. A round-trip engineer ensures that when changes are made to the model, they’re reflected in both areas.
Once you’ve created your data model, you’ll need to be able to import and export it as needed.
You should be able to take pictures or screenshots of any diagram on the screen so that you can share them with others or store them for future reference.
When using a data modeling tool, you should be able to define business vocabulary terms and map them to their usage within your model. These definitions ensure that people across the company use similar terminology and concepts.
Data modeling tool users should be able to break down their models into subsets and then validate these pieces of the whole against common requirements. Validation gives you an idea of whether or not your model meets some specific criteria before deploying it live.
One of the most valuable things about having a data modeling tool is being able to locate certain parts of your model quickly. To do this, you need an object search function that will scan the entire document for anything matching specific criteria.
Ideally, your data modeling tool will interface with other software programs. Doing so saves time because administrators can then automate many tasks.
Whether you want to create a new model from scratch or modify one of your existing models, you should always be able to connect directly to the relevant database for whatever task.
Reports provide valuable insights into how your system is functioning; it’s important to have a data modeling tool that makes creating them easy. Reports are usually generated by querying the underlying database and turning the results into something readable. They may contain any number of charts, such as bar graphs, pie charts, scatter plots and line graphs.
Charts offer another way to gain insights into how well your system works by presenting quantitative data intuitively.
Data modeling tools are a critical part of the modern business world, especially for data extraction, management and preparation for reporting. In order to use these tools effectively, it is important to understand the more specific benefits they offer your company.
SEE: Job description: Big data modeler (TechRepublic Premium)
For starters, data modeling can be used in both the pre- and post-processing phases of the data analytics process. As an example, data modeling can be used as a pre-processing technique to extract raw data from different sources in order to build unified datasets for analysis.
Once you have created these datasets, you can better combine them for more powerful insights. As a post-processing technique, data modeling can provide enhanced detail that users cannot glean through descriptive statistics alone. In addition, by using the advanced visualization tools that come along with data modeling software, analysts can quickly see relationships within their datasets in previously impossible ways.
These tools allow analysts to sort by specific variables, drill down into aggregated categories, pivot rows and columns, explore dimensions like time or geography, or filter results by keyword search. Data modeling tools also simplify tasks like extracting and inserting data into relational databases, building complex queries without writing code, generating accurate projections without heavy calculations and converting unstructured data formats into tabular structures.
And finally, data modeling software allows increased transparency on all levels of the analytical process, which is an important step toward true data democratization in your organization. These tools are becoming increasingly imperative to staying competitive in today’s market.
Learn the latest news and best practices about data science, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence.
Top data modeling tools of 2022
Your email has been sent
Your message has been sent
TechRepublic Premium content helps you solve your toughest IT issues and jump-start your career or next project.
Windows 11 gets an annual update on September 20 plus monthly extra features. In enterprises, IT can choose when to roll those out.
Edge AI offers opportunities for multiple applications. See what organizations are doing to incorporate it today and going forward.
This is a complete guide for Apple’s iPadOS. Find out more about iPadOS 16, supported devices, release dates and key features with our cheat sheet.
Discover data intelligence solutions for big data processing and automation. Read more to explore your options.
Whether you are a Microsoft Excel beginner or an advanced user, you’ll benefit from these step-by-step tutorials.
This document helps make sure that you address data governance practices for an efficient, comprehensive approach to data management. This checklist from TechRepublic Premium includes: an introduction to data governance, a data governance checklist and how to manage a data governance checklist. From this checklist’s introduction: Data governance is the process by which an organization …
Recruiting a Scrum Master with the right combination of technical expertise and experience will require a comprehensive screening process. This hiring kit provides a customizable framework your business can use to find, recruit and ultimately hire the right person for the job. This hiring kit from TechRepublic Premium includes a job description, sample interview questions …
Knowing the terminology associated with Web 3.0 is going to be vital to every IT administrator, developer, network engineer, manager and decision maker in business. This quick glossary will introduce and explain concepts and terms vital to understanding Web 3.0 and the technology that drives and supports it.
While the perfect color palette or the most sublime button shading or myriad of other design features play an important role in any product’s success, user interface design is not enough. Customer engagement and retention requires a strategic plan that attempts to measure, quantify and ultimately create a complete satisfying user experience on both an …
- Published in Uncategorized
Employee Monitoring: How to (and not to) track employee productivity – Business Management Daily
Enter your email address to instantly generate a PDF of this article.
Before 2020, employee monitoring in a traditional office environment was pretty straightforward. Managers and supervisors kept track of employee performance and productivity by directly monitoring them throughout the workday. Yet, the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020 threw a wrench into this tried and true system for most companies.
In a few short months, nearly every business had to incorporate a remote workforce of some capacity to continue functioning. Before the pandemic, only 6% of employees were remote workers. As early as May 2020, one-third of all employees began working from home.
This fed the need for new ways to track employee activity, as managers could no longer directly monitor their teams in person. Beyond that, droves of companies that were inexperienced with remote work were creating monitoring policies for the first time. That led to the creation of numerous employee monitoring solutions, including computer monitoring through cloud-based software, GPS tracking, keylogging, and other methods.
Yet, the advent of more rigorous ways to monitor remote employees has led to some backlash and privacy concerns, such as watching employees through their webcams. Despite the concerns, it’s clear that remote work is here to stay. When polled, a mere 6% of workers said they wanted to go back to working entirely on-site. Instead, it seems that a hybrid of remote work and on-site work is the way going forward, with 74% of U.S. companies either already using a hybrid approach or planning to incorporate one in the future.
Since employee monitoring is such a big issue today, I’ve put together this guide on properly implementing employee monitoring without violating anyone’s privacy. Read on to discover the most successful types of workplace monitoring for both remote workers and office workers.
While the pandemic skyrocketed employee monitoring into the mainstream, it’s not a new concept. Not only that, but certain businesses have used employee monitoring software for many years before 2020. An example would be call centers, where employee phone calls and voicemails were recorded and closely monitored to ensure their quality and efficiency.
Customer support is another industry where employee monitoring tools have long been the norm. If you’ve ever called a customer support line, you’ve likely heard the classic automated phrase, “This call may be recorded for quality assurance or training purposes.”
Well, that’s a classic form of employee monitoring right there. Companies would record customer support calls to ensure customer satisfaction and use them for future employee training.
For example, suppose they found an exemplary customer support call where the employee was courteous and knowledgeable. In that case, they’ll likely include the recording in training for new employees so they’ll know what a successful call sounds like. Conversely, they could also pick a poor customer support call to use in future training as an example of what NOT to do.
Post-COVID-19, many employee tracking software programs started popping up, allowing companies to track employee productivity, computer activity, emails, and even individual keystrokes.
Let’s look at the most common methods for employee monitoring for remote, mobile, and on-site workers.
Has your workforce gone almost entirely remote since 2020? Have you been scrambling to find a way to track key performance metrics without invading employee privacy? If so, there are plenty of employee monitoring systems that allow you to discretely keep track of tasks, work hours, quality of work, and more.
That can help you salvage your productivity and regain control over your workforce without coming off as a tyrannical micromanager. That said, there’s a fine line between healthy employee monitoring and invasive workplace surveillance, so you must be careful. Here are some of the most popular methods for measuring the productivity of your remote workforce.
When working from home, sometimes the temptation to surf the internet for personal reasons can become too great. In small doses, this isn’t too big of an issue. However, if left unchecked, internet surfing and app usage can dramatically affect employee productivity.
For example, say you notice that an employee is frequently late getting back to clients, misses deadlines, and not communicating. In this case, being able to track their URLs and app usage can come in handy. That way, you can discover if they’ve been wasting time on YouTube or Instagram excessively during work hours. The usefulness of these tracking features doesn’t end there, though.
On the other side of the spectrum, say that you notice an employee is falling behind — but it’s not due to wasting time. After checking their internet history and app usage, you discover that they’re struggling to use a new piece of software properly. From there, you can hook them up with the proper training to increase their productivity.
To take things a step further, you could also incorporate web-filtering and URL-blocking features. For instance, if you don’t want employees checking their social media during the workday, you can choose to restrict sites like Facebook and Instagram (you can also block sites containing inappropriate content).
Certain types of employee monitoring software allow you to enable ‘time-wasting’ sites like Facebook and YouTube, but only for a
limited period. Others have special tracking features for social media sites, where you can view specific employee actions.
These features come in handy for tracking positions like social media managers, where the job requires them to use apps like Facebook. However, the special tracking features will let you know if they’re doing their job on social media or are checking their personal feeds.
A significant concern most companies have with remote work is they can’t monitor employees in real-time like they could in the office. They feel that there’ll be a steep dropoff in employee productivity, which doesn’t have to be the case.
That’s a big reason why many employee monitoring programs began to offer screenshots, screen sharing, and video monitoring as part of their features. Screen sharing of an employee’s computer will update managers on an employee’s progress on tasks, emails, and other workflows.
This type of employee monitoring is excellent for project management, as it makes tracking progress on individual tasks a breeze. That can also save money, as a supervisor can quickly see if an employee is on the right track with a project or not.
Without a form of monitoring in place, the employee may embark down the wrong path, which can derail progress on the project and cost valuable resources to fix.
The most effective form of screen sharing is only interested in tracking the work getting done on the device through tracking timesheets, user activity (levels of engagement during the day), performance metrics, and other non-invasive ways to measure productivity.
Legal issues and concerns over webcam surveillance
Video surveillance is an area that gives many remote workers privacy concerns. For one, many remote workers worry that their employers are spying on them through their webcams.
So is Big Brother keeping an eye on everything you do and say at work?
Let’s look at what the law says to find out.
The Electronic Communications Privacy Act (ECPA) of 1986 is the guiding piece of federal legislation in this regard. It states that employers have the legal right to monitor employees’ verbal and written communications for any business purpose. That’s especially true if the communications are made via company equipment (laptops, phone systems, etc.).
The key takeaway here is that employers are allowed to keep track of your business-related activities, not personal ones. That means it’s illegal for them to record your personal calls made on your smartphone.
Besides monitoring verbal and written communications, employers can integrate further monitoring methods — but here’s the caveat — with employee consent. That means if a company doesn’t have a written policy stating that they’ll watch employees on webcam, they likely aren’t doing it secretly. In fact, it would be illegal to do so.
Also, the ECPA is a federal law, and some states have additional laws that value employee privacy even more. You should check the regulations for your state to find out if you’re protected from certain forms of monitoring or surveillance.
Another way to monitor remote employees is to use time tracking or file tracking software. Software with time tracking features allows employees to control when they clock in and clock out. As such, they’re free to clock out to take a break whenever they need it (with managers having the ability to track work hours and breaks, of course).
This type of employee monitoring is both effective and empowering, as it places the onus on the employees to keep track of their own time. That’s a great way to track employee progress without worrying about violating their privacy.
Besides clocking in and out each day, time tracking features also allow employees to track hours spent working on specific projects and tasks. As a manager, that makes it effortless to find out how much work got done on any given day. You’ll be able to see when everyone started work, what they worked on, and how long they spent working on it.
That eliminates a lot of the guesswork involved with monitoring remote workers, which is a definite plus. Not only that, but time tracking data is also invaluable for making more accurate time estimates and budgets for future projects and tasks.
File tracking uses and benefits
A deeper version of time tracking is file tracking, where employers receive detailed reports on which files were worked on, by whom, and for how long. That comes in handy when most of the work done at your organization is completed through files, such as Word documents or spreadsheets on a shared drive.
File tracking has other benefits as well.
For instance, with file tracking software in place, you won’t have to spend hours looking for lost or misplaced files. You’ll be able to follow a detailed trail of where the file has been and who scanned it/edited it last.
Another area where file tracking comes in handy is with audits. As an organization, it’s crucial for employees to follow your policies for document handling and retention. Otherwise, you’ll wind up with documents and files scattered all over the place, which spells disaster for an audit.
With file tracking in place, any gaps in the audit trail will surface immediately, as you’ll instantly know if a file has been misplaced, lost, or handled incorrectly. That can help save time and reduce costs due to the boosted efficiency.
Last but not least, file tracking will tack on additional security for all your files and documents. Certain industry regulations require highly specific document handling procedures. For instance, some legal or business files containing sensitive information can only be accessed by authorized parties — the violation of which is a crime.
With file tracking, you can automate security alerts to trigger when an unauthorized user attempts to access one of these documents. You can also set up automatic alerts when someone tries to move sensitive documents from their secure location.
Another form of employee activity tracking is keystroke logging.
What’s that?
Keylogging programs record each individual keystroke of an employee during their work hours. Keystrokes are how you communicate with your computer, and more goes into monitoring them than you might think.
For instance, did you know that the velocity of your keystroke is a measurable metric? Or that keyloggers also track the length and time of the keypress? Time, length, velocity, and the name of the key are all metrics that a keylogging program will track.
Why is this valuable information?
It is because you can decipher quite a bit from interpreting a user’s keystrokes. Employers can use keylogging to keep track of individual tasks, workplace communications, and more. Yet, keylogging has a notable dark side, and some view it as an outright violation of employee privacy in all its forms. The primary concern is that keylogging will reveal quite a bit of sensitive employee information.
For instance, if you’re keystroke logging an employee, it’s not uncommon for them to type their:
Personal address
Social security number
Credit card/debit card number (if making a business purchase to be reimbursed for later)
Company passwords
Private messages
As you can imagine, all this private information would be disastrous in the wrong hands. That’s why lots of keylogging programs are used for nefarious reasons, such as identity theft. For these reasons, many employers have stopped using keylogging programs entirely, as they believe the security risks outweigh the benefits.
Not every employee is going to work from home — but employee monitoring is still a necessity. Also, some positions don’t involve working from home OR at an office.
Delivery drivers are an example of this, as their vehicles are technically their offices. As you can imagine, this type of work requires a particular kind of monitoring. Most companies like Uber and DoorDash use GPS tracking to monitor productivity, efficiency, and timeliness of delivery.
There are also types of employee monitoring that take place in the office but don’t involve the physical presence of managers or supervisors. Let’s take a look at the most common types of employee monitoring for office employees and mobile employees.
Over 50% of all companies monitor employee emails, which is an effective way to prevent potential issues before they occur.
How is that?
Let’s say a particularly disgruntled employee has had enough and is ready to quit. However, before leaving they decide to leak a ton of company trade secrets to a competitor out of spite. With an email tracker in place, you could intercept this damaging email and delete it before it gets the chance to do any harm.
That’s an extreme example, but it conveys the power of monitoring employee emails.
Remember, the Electronic Communications Privacy Act states that it’s legal for companies to track all verbal and written communications, and email definitely falls within that umbrella. So you shouldn’t be surprised if you discover that an employer is tracking company emails, as it’s well within their federal rights.
Another use for tracking employee emails is that it can help settle disputes. An example would be examining employee emails to determine whether a case of sexual harassment took place or not.
Proponents of this monitoring technique state that it’s invaluable for protecting sensitive information from leaving the company and falling into the wrong hands.
Email monitoring isn’t without its critics, though.
Detractors of this method state that email monitoring builds feelings of distrust and resentment among employees. They may feel that you don’t trust them by reading their emails, which can hurt workplace morale. There is evidence to back this up, too.
A study by Gallup found that employees that felt disengaged were more likely to leave the organization. A high turnover can destroy your productivity, so it’s best to be transparent with employees about email monitoring. In particular, let them know that it’s to ensure consistency in your messaging, not because you don’t trust their abilities.
You may also wish to share the frequency of such monitoring. For example, employee emails may be tracked but only pulled in the case of a specific incident. In that situation, it may raise good will for employees to know that you’re not regularly looking over their communication.
If you’re in charge of delivery drivers, you likely already have some form of GPS tracking in place at your company. In today’s age, employers can use GPS trackers on more than just company vehicles, too. Location trackers also exist for work phones and tablets, which are primarily used to track the work of sales representatives.
This technology enables managers to always know where their employees are when they’re on the clock.
Besides monitoring employee locations in real-time, location trackers also allow managers to view historical data, such as the routes chosen for customer deliveries. That will make it easy to identify the quickest and most reliable routes for drivers to use in the future.
Another advantage of implementing GPS trackers is you can quickly confirm if a package was delivered or not. If the customer reports no delivery, you can consult the location tracker data to see if a driver made it to their property with the package.
Then there’s the additional safety that GPS trackers provide to mobile employees. Should a driver go missing or get into an accident, the location tracker can quickly triangulate their location to send help.
Other uses for location tracking software
Construction contractors and companies with field service teams (plumbing, locksmiths, HVAC, landscaping, etc.) also use location tracking software, albeit in a different way than delivery driver managers.
Contractors use GPS software to confirm that their crew arrives on-site when they’re scheduled. They can also analyze the data to estimate arrival times for clients better.
For instance, if they notice that their crew has a more challenging time getting to a particular part of town (either due to heavy traffic or another issue), they can quote customers a later arrival time to accommodate the delay.
That will help you avoid disappointing customers due to your crew arriving late, which will improve your customer satisfaction rates.
Call centers and customer support teams have long had these forms of employee monitoring in place. Yet, they aren’t the only ones incorporating recorded phone calls to keep track of business communications.
Procurement managers may also choose to record employee phone calls with suppliers.
Why is that?
Healthy supplier relationships are integral to the success of the procurement process, which is why managers may choose to monitor their calls to ensure employees are being cordial, helpful, and polite with suppliers.
Sales teams may also choose to record client calls to monitor the quality of their selling techniques and phone etiquette. After combing through the data, sales managers can identify the types of calls that are the most effective at converting prospects to use in future training.
Monitoring voicemails has become far less common, as the practice of leaving voicemails has become antiquated. If clients or suppliers don’t answer their phones, it’s far more common for employees to send an email or instant message instead of recording a voicemail.
Speaking of instant messages, it’s common for employers to monitor messages that get sent through apps like Slack.
For the most part, IMs have replaced voicemails (and even emails in some cases) due to how quick and efficient they are to use. If you need to quickly notify a coworker of an upcoming meeting or task that’s due — nothing beats sending them a quick message via instant chat.
Tracking employee IMs is primarily effective at resolving in-house disputes and issues.
For instance, if an employee claims a coworker is bullying them in the office, checking the IMs of the associate in question is a reliable way to uncover evidence.
Employee monitoring software often has features that enable managers to view employee IMs both in real-time and for future use.
Lastly, some businesses choose to use closed-circuit TV cameras to monitor their property and the performance of their employees. It’s common for establishments to place cameras in areas where employees aren’t supposed to be (such as food storage or money vaults).
Some businesses set up CCTV cameras around the office to encourage better performance from their employees, but this can lead to trust and privacy issues, so it’s not recommended.
CCTV cameras are also valuable for protecting properties at night and acting as a deterrent for thieves.
By now, you should be more familiar with the different types of employee monitoring, both for remote work, mobile work, and for on-site workers.
While any form of monitoring is bound to raise privacy concerns eventually, employee monitoring can be a useful tool when implemented properly. Over monitoring could harm employee morale. However, the right amount of monitoring can ensure productivity and provide valuable data.
The pandemic in 2020 catapulted remote work monitoring into the mainstream, with many companies now adopting different types of employee monitoring software.
It’s best to focus only on monitoring work hours, task completion, and employee communications to avoid privacy concerns. Not only are these the most effective metrics to monitor, but they’re also well within your rights, as stated by the ECPA.
Instantly access free expert advice, management strategies and real-life examples of workplace success.
- Published in Uncategorized
20 Best Document Signing Software (New Edition 2022) | by Toby Kiernan – DataDrivenInvestor
DataDrivenInvestor
Jun 1
Save
The use of paper forms of documentation is rapidly dwindling. Increasing numbers of governments are realizing that going paperless saves both time and money. If a document is legally binding, it doesn’t need to be physically signed by the parties involved.
It was the COVID-19 epidemic that spurred the majority of companies to adopt paperless. Electronic document signing software has been embraced by businesses at an astronomical rate. The use of electronic document signing software makes it possible to digitally sign key documents such as contracts and invoices.
The use of best document signing software will only grow in the future. A snag in this adoption, however, is the need to select the appropriate electronic document signing software free.
There are a number of programs that allow you to type, draw, and digitally add to the papers, making this procedure difficult.
With so many options for the best electronic document signing software, it’s no wonder that the workplace is becoming digital. As part of the workplace’s digitalization, it encompasses technologies like corporate mobility, digital information management, and more.
As soon as you’ve landed on this page, we’ll walk you through the process of selecting the best document signing software for business.
The best document signing software for small businesses may be found in the list provided below.
➤ CEO — Borya Shakhnovich
➤ Mobile App: iOS | Android
➤ Location — Brookline, Massachusetts
To sign and submit papers electronically, there is no better program than this one. Automating and optimising operations, gaining access to payments, and keeping track of paperwork are all made easier with its support.
Reusable templates in this program make mailing papers a breeze and a time saver. SignNow’s workflows let you bundle documents and transmit them to specific people depending on their roles. After signing a document, SignNow allows you to choose from a variety of options for how the document will be handled.
➤ CEO — Ryan Pegram
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — Thornton, Colorado
WeSignature is a current example of best document signing software for business that allows users to digitally sign papers. This app has been used by a large number of professionals for both personal and professional reasons.
Individuals and businesses may sign a wide range of online documents using this easy, fast, and painless program. The WeSignature software allows you to sign documents, fill out paperwork, and follow up with the recipients on a regular basis once you’ve adopted the program.
For years, it’s been the greatest tool for electronically document signing in the industry. Once you start utilizing WeSignature, you’ll be amazed at how quickly your documents will be delivered. With the use of this technology, enterprises may send out a large number of papers simultaneously.
➤ CEO — Will Cannon
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location —340 S Lemon Ave Ste 1760 Walnut, CA 91789
Signaturely is another popular best document signing software. Many individuals choose it when they want a quick and easy approach to get their documents officially signed. The ease with which it may be used makes Signaturely a standout. Online document signing is made simple with our user-friendly and speedy platform.
Signaturely is unique in that it focuses on removing features rather than adding new ones. It focuses on streamlining the signing process by eliminating any stages that aren’t absolutely essential.
➤ CEO —Dan Springer
➤ Mobile App: iOS | Android
➤ Location — San Francisco, CA
DocuSign, with its electronic document signing capabilities, is also a preferred platform. One of the key reasons why the firm has been able to maintain its position as a market leader is because of its simplicity of use.
DocuSign makes it simple to upload documents, add a signature box, and email signed documents to recipients. Teams may easily sustain momentum when sending and receiving critical papers as a result of this.
If you use Google Docs or any other spreadsheet for business, you can easily create electronic signatures using DocuSign and your Google Drive account.
You may use DocuSign to electronically sign papers that can be readily integrated with a wide range of products since it is simple to use and straightforward to understand.
➤ CEO — Joseph Walla
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — San Francisco, CA
Document signing software like HelloSign is highly regarded for the unique capabilities it offers. It excels in the areas of personalization, client service, and pricing flexibility. Embedding and branding the signature alternatives in the papers is also made possible by the API.
It also offers a wide range of extensions and integrations that are compatible with all major online signing rules. It is the greatest electronic document signing software owned by Dropbox, and it has excellent connectivity with many other products, like Google Suite, Gmail, and more.
➤ CEO — Shantanu Narayen
➤ Mobile App: iOS | Android
➤ Location —San Jose, CA
With Adobe Sign, you can manage your processes from any place and on any device because of its feature-rich software. Using this program to sign papers is a common practice because of the ease with which it creates an electronic signature in word format.
In addition to its focus on worldwide compliance, Adobe Sign is noted for its extensive interaction with third-party applications. For both electronic and digital signatures, it has a wide range of options.
➤ CEO — Mikita Mikado
➤ Mobile App: iOS | Android
➤ Location — San Francisco, California
Electronic document signing software like this one is well-known for its user-friendliness and simplicity of use. A free document signing software for business that aids in document management is provided by this service. There is also an automatic workflow, audit history, as well as a drag and drop connection included.
Additional interfaces include CRM, file storage, and payment options for PandaDoc users. The contract management software PandaDoc is worth a try for those searching for an efficient solution.
➤ CEO — Martin Holmstrom
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — Portland, Oregon
Electronic document signing software free that is utilised by a large number of companies. Many hours may be saved by using this service, which is also consistent with e-signature requirements.
In addition to document monitoring, configurable workflows, and automated reminders, this tool offers a free plan.
➤ CEO — Sunil Patro
➤ Mobile App: iOS | Android
➤ Location —Brookline, Massachusetts
This is another excellent electronically best document signing software for business. It’s one of the greatest apps for personal usage of electronic signatures. You may begin uploading papers, preparing them for signatures, and submitting them immediately after signing up for a free trial.
SignEasy is compatible with a broad range of third-party apps and can be easily integrated into your existing workflows. You don’t have to worry about opening, signing, and sending documents using Gmail. Finally, you may take use of a variety of features, like automated reminders, tracking, and signature sequences, among others.
➤ CEO — Julian Zehetmayr
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — Wien, Wien
If you need legally enforceable electronic signatures but don’t want to spend a lot of money, Eversign is a perfect option for you. For a low monthly subscription, you can send a large number of documents without incurring additional charges.
Audit trails, contract management, and app connections are all included in Eversign’s basic features. If a company is trying to expand its user base, or if it wants additional incentives like in-person signing, there is no additional cost.
➤ CEO — Daryl Bernstein, Cary Dunn, and Jonathan Siegel
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — Fort Lauderdale, FL
Electronic signatures are quick, simple, and secure using RightSignature. It’s one of the greatest solutions for mobile electronic signature software since no apps need to be downloaded or installed. With RightSignature, you can drag and drop form fields into PDFs, much like other document electronic signature providers.
Multiple papers may be submitted simultaneously, as well as templates created and shared with others. Documents may be sent out and signatures requested in a certain order.
Custom branding, team stats, and the option to request signer attachments are included in the higher-level plan. While RightSignature’s connectors and partner options are attractive, the company falls short of interacting with a more diverse technology stack.
➤ CEO — Mahender Bist
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — Cupertino, California
Even if the price of eSign Genie appears to be a bargain, it’s actually a high-quality digital signature service. eSign Genie, despite its modest price, is packed with features that make the e-signing process easier and more convenient for both signers and corporations. Connecting to eSign Genie is as simple as establishing a network connection and using the form signing tools.
As opposed to alternatives like PandaDoc or GetAccept, eSign Genie can help you collect electronic signatures at a fraction of the expense. The pay-as-you-go option for infrequent clients is one of the most interesting parts of the business. Additionally, the Professional plan allows for the signing of documents in person and assigning signers, both of which are generally reserved for more expensive e-signature programs.
➤ CEO — Geert-Jan Persoon
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — Amsterdam, Noord-Holland
For senders that need to distribute several documents each month, SignRequest looks to provide a lot of functionality and customization choices.
A post-signature landing page and the option to change the document signing sequence are all included in the Professional plan when generating documents for multiple signers. For small business owners that don’t need to send a lot of paperwork each month, this platform has everything you’ll need to get your docs out there.
SignRequest’s document management features make it easy to keep track of what paperwork is still pending and what paperwork has been completed.
With the ability to create templates, collect signer attachments, and even select the authentication mechanism your signatures may utilise to authenticate themselves, SignRequest is a best document signing software for business or anybody looking for a quick and easy way to sign.
➤ CEO — Ron Cogburn
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — 2701 E. Grauwyler Road Irving, TX 75061, USA
You may use it with a wide variety of business apps thanks to its cloud-based best document signing software for business, it may help speed up internal and external sign offs, decrease the need for paper procedures and boost team efficiency.
DrySign is compatible with Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, and Salesforce. At the same time, it may be used on desktops, laptops, and mobile devices.
This approach conforms with a number of electronic signing requirements, including the ESIGN Act and the UETA. Smart tracking, audit trails, and multi-factor authentication are provided in DrySign in order to help enterprises lower the risk associated with their transactions.
Thanks to the platform’s dashboard, all documents and activities may be viewed at once. It is possible to request multiple signatures, establish automated notifications, view changes in real time, alter document fields and upload bulk files, and many more options are available.
➤ CEO —Vasiliy Ivanov
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — Bronx, New York
Using KeepSolid Sign, users may electronically sign a variety of documents, including contracts, transactions, and other types of agreements. This product may be set up in the cloud or on-premises.
It is possible to sync documents across several devices, such as PCs, tablets, and smartphones, using KeepSolid Sign. AES-256 encryption is used to safeguard the data in the system. The firm also offers mobile apps for iOS and Android devices.
It is possible for users to sign and annotate files even while they are not connected to the internet, and the edits are then kept. An activity dashboard supplied by the service allows users to keep tabs on the progress of a particular document.
➤ CEO — Samir Smajic
➤ Mobile App: iOS | Android
➤ Location — 2261 Market St #4358, San Francisco, CA 94114, USA
When it comes to sales teams of all kinds, GetAccept’s cloud-based document signing software. Papers like as contracts, agreements, personnel files, and personal documents may all be signed electronically using this system. Sales professionals can give personalized support to their customers thanks to GetAccept, which automates the sales documentation process.
With GetAccept, sales proposals may be accompanied by video presentations. A document analytics tool lets users see when a document is accessed and keeps track of how many times it has been viewed. For those who are interested, they may also observe which parts of the document were the most popular with the receiver.
Customer relationship management and marketing automation systems are compatible with GetAccept’s integrations. Contracts and other papers can be saved for future reference. Signatures may be renewed at any moment, and they can be imported at any time. GetAccept includes a live chat option as well.
➤ CEO — Matthew Moynahan
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — 121 W Wacker Drive, Suite 2050, Chicago, IL, 60601, United States
Onespan Sign is another best document signing software that are legally binding. Your bank account or insurance policy application may have been signed via OneSpan Sign without your knowledge. OneSpan’s customers can completely white-label the e-signature process so that their brand is always in the limelight, from beginning to end, resulting in high completion rates.
While OneSpan’s e-signature technology has been employed by some of the world’s most security-conscious enterprises (such as IBM and NASA), the company is recognized for its focus on security and compliance.
According to Gartner, OneSpan Sign is also a leading provider of electronic documents signature software for businesses of all sizes.
Fair pricing and willingness to go the additional mile for clients of all sizes are hallmarks of OneSpan’s business model.
➤ CEO — Stephen Curry
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — Singapore
Over the past few years, CocoSign has emerged as an extremely renowned online electronic document signature software. It is one of best document signing software for business for sending, signing, saving, and accessing documents online.
It is capable of automating business processes by closing deals quickly, safely, and legally.
CocoSign enables users to choose a free trial for understanding how the platform should work and how useful it can be. It is easily the best place for online signatures as it improves businesses by automating significant parts of business deals. It is empowered with multiple applications, integrations, APIs, and industry-specific solutions.
CocoSign allows you to get signatures digitally without facing problems in managing paperwork. It provides a user-friendly, digital, and integrated experience for creating e-signatures.
In addition, it also offers cross-platform functionality and can be accessed anywhere. People use it because it is safe, legally compliant, and efficient.
➤ CEO — Jessica Kelly
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location — 700 N Valley St Suite B Anaheim, CA 92801
DigiSigner is a cloud-based electronic document signing software and one of the best PandaDoc alternative that focuses on speed, affordability, and convenience of use.
Using the service, businesses and people can sign contracts and agreements from any location in the world, regardless of their location.
DigiSigner is compatible with a wide range of devices, including laptops, tablets, smartphones, and more.
All main e-signature laws, such as ESIGN, UETA, and European eIDAS, are met by DigiSigner.
DigiSigner’s signatures are legally binding and can be used in a court of law.
➤ CEO — Jay Jumper
➤ Mobile App: None, web-based only
➤ Location —Chattanooga, TN
A next best document signing software is SIGNiX, which makes it easy for partners in highly regulated industries like real estate, wealth management, and healthcare to use digital signature and online notarization software together.
There are no costs or risks to using the patented SIGNiX FLEX API.
It allows partners to offer military-grade cryptography, enhanced privacy, and permanent legal evidence of a true digital signature without having to deal with paper-based processes.
Using the best document signing software for business to electronically sign papers in the future will save both time and money, making it a need in the near future. Using online document signing software, businesses may keep track of their activities and even set reminders.
Using online best document signing software makes it possible to enhance your journey and provide a helpful signing experience. Take your time, learn more about the applications we’ve already listed, and make an informed selection before committing to one of them.
Subscribe to DDIntel Here.
Join our network here: https://datadriveninvestor.com/collaborate
—
—
empowerment through data, knowledge, and expertise. subscribe to DDIntel at https://ddintel.datadriveninvestor.com
Marc Kenneth Lomio & Melrose Mejidana
cloudworm
Girls in Crypto
Kevin Kononenko
in
Mission.org
Will Velida
OCE blogger
in
Oracle Developers
Logic20/20
Gustavo de Paula
in
Having Fun
AboutHelpTermsPrivacy
I’m interested by human creativity and technology. Nature enthusiast, self-motivator, visionary, and energetic communicator. Email me: tobykiernan1984@gmail.com
Help
Status
Writers
Blog
Careers
Privacy
Terms
About
Knowable
- Published in Uncategorized
Meet LINK: The Easy Way To Handle All Your Document Workflows On Your Mobile Device In A Single App – Above the Law
Subscribe and get breaking news, commentary, and opinions on law firms, lawyers, law schools, lawsuits, judges, and more.
When was the last time you went to work (or anywhere, really) without some kind of mobile device with you? Since the adoption of mobile devices, the answer is probably never. When was the last time you felt you could adequately handle all your work on that mobile device? If you’re like most lawyers, the answer is, again, probably never.
The legal profession today is a mobile one, with attorneys practicing anywhere and everywhere with the help of smartphones and tablets. As ubiquitous as they are, though, most lawyers would say they can’t handle all the meaningful work they need to handle on those devices, due to poor document workflows, security concerns, and usability.
What if I told you that you really could handle all your work in one app on your mobile device? It might sound too good to be true, but it’s possible with the LINK app from Mobile Helix.
LINK is finally making it possible to handle documents in a meaningful way on all your devices. LINK combines convenient workflows, document management, search, review, annotation, comparison, editing capabilities, and email management in one app that you can actually use from your phone or tablet.
Do Everything, Everywhere With LINK
When you think about the tools you use most in your day-to-day work, your document management system (DMS) and Outlook are probably at the top of the list. Working in both on your mobile device, though, has historically been a huge struggle, if not impossible. LINK brings them together in a single, secure, easy-to-use app.
LINK is designed to support the workflows attorneys use all day, every day. The app works with today’s most popular mobile devices – iPhones, iPads, and Android phones and tablets – and supports the three leading document management systems, iManage Work®, NetDocuments, and eDocs by OpenText.
LINK is solving the pervasive problem of lawyers being unable to adequately work on their mobile devices. With LINK, lawyers can fully access their documents, compare them, mark them up, edit them, email them, and more, as easily and securely as they can on a computer.
LINK’s Top Features for Simpler Workflows
Lawyers have long asked for a way to be able to work with their critical documents on their mobile devices, only to be disappointed – until now. LINK is a game-changer when it comes to on-the-go document workflows.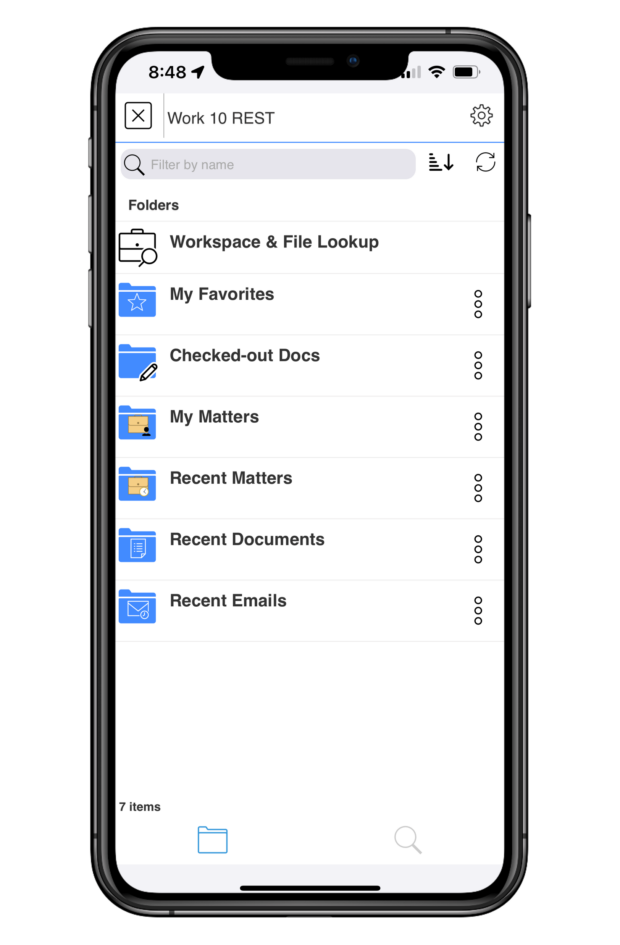
Through LINK, lawyers can not only securely access all documents in their DMS, but also do all the work they need to do directly in those documents, even if they’re on a mobile device far from the office.
Access Full DMS Functionality
When you launch your DMS from within the LINK app, you’ll see everything you’re used to seeing – documents, folders, matters, and more. LINK makes it possible to navigate your DMS from the palm of your hand, just as you always have.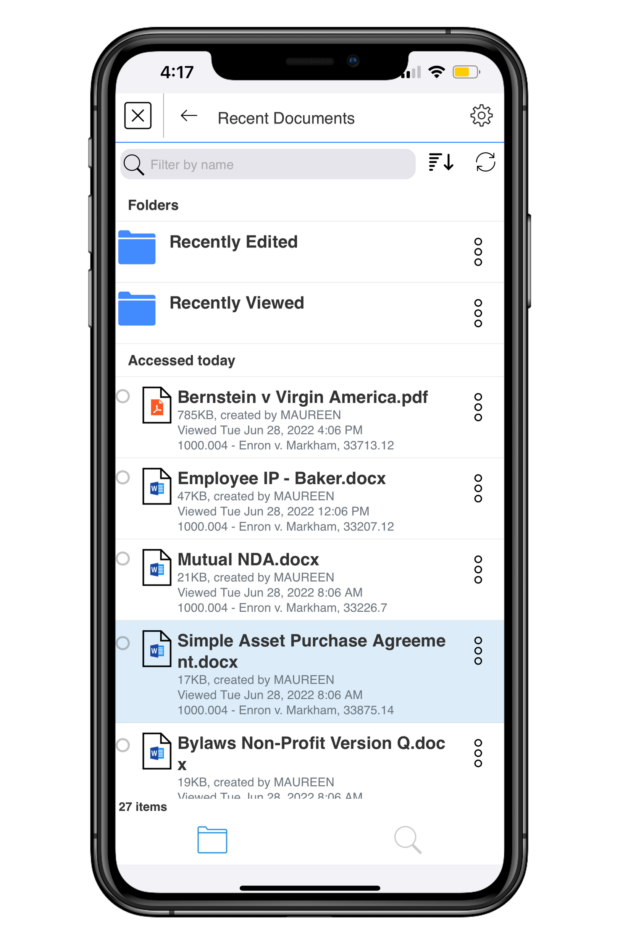
Locate the document you want to work on by finding it in your organized folders or search for it using LINK’s simple yet robust search functionality or Quick Lookup feature.
Once you’re in the document, LINK gives you the tools you need to meaningfully work on it from your mobile device. On tablets, LINK offers a useful split-screen mode, so you can have multiple documents or applications open on your screen at the same time, with multiple live tabs on each screen.
You can choose to open a document in the Microsoft Word app with LINK and edit your documents directly. Just check them out of your DMS with LINK, edit with Word, and then check them back in when you’re done. Any editing you do via LINK will automatically be saved and will be there when you access the document again in your DMS on your computer or via LINK on your mobile device.
When you’re done working on a document and want to share it with others, you can email it directly from your open document. You can also choose to AirPrint the document directly from the app.
LINK prepares the email for you, and you simply click send. Documents are sent in either their original file formats, as PDFs, or as proprietary links from your DMS that keep them secure. These links can’t be accessed via ordinary email systems, which has long been a limitation on mobile document work. LINK decodes those links, giving you full, secure access to your documents.
Finally, LINK offers encrypted document storage through My Files. You can find your latest work in your Recently Viewed folder and even access those documents when you’re offline. LINK automatically saves your work for you, so you never lose anything important when you’re on the go.
Document Annotation
LINK allows you to annotate documents directly in the app, without having to switch apps in order to mark up your document. Just tap the paper and pencil icon to get started.
LINK offers several annotation features. You can write on your document with an Apple Pencil, highlight portions (in the color and opacity of your choice), outline specific text, strike through text, bookmark your page, add text notations on the document, sign a document, and add stamps for time or date. When viewing the document, you can adjust its appearance, including a dark mode option, how large your margins are, how you want the pages to scroll, and more.
Once again, when you’re done annotating, you can AirPrint your document, upload it to your DMS, or email your markup. LINK gives you the full ability to annotate your document right from your mobile device, wherever you may be.
Document Comparison
Having the ability to compare two documents or two versions of the same document is critical, but it has long caused headaches and required jumping between different apps. With LINK, it’s simple. Right in the app, you can compare two versions of the same Doc ID or any two documents in your DMS. LINK takes its document comparison capabilities even further by letting you compare documents attached to emails to any documents in your DMS or Outlook.
Email Management
LINK not only helps with document workflows, but with email management as well. Directly through the LINK app, you can search for emails in Outlook and file your emails to your DMS.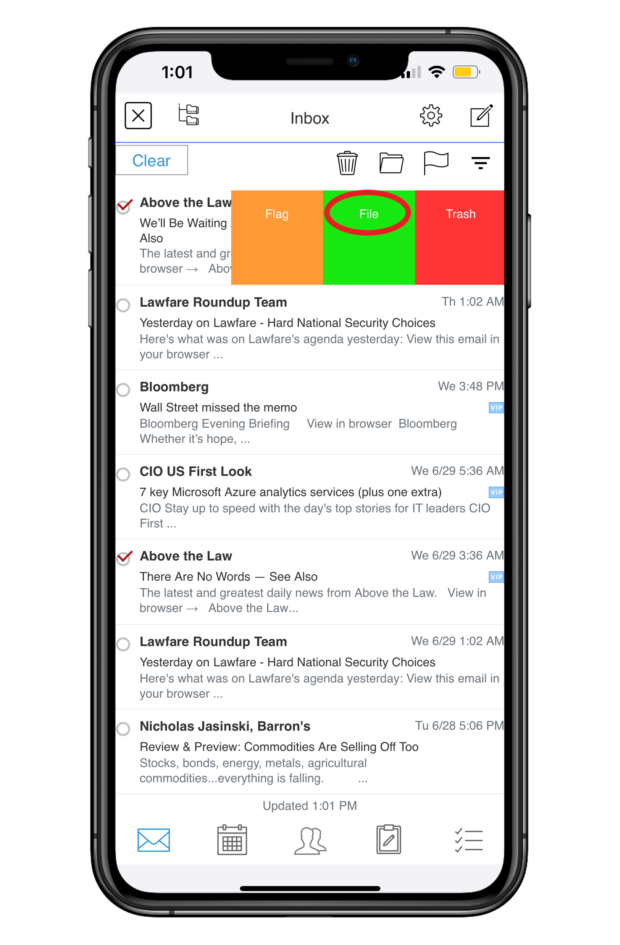
You can file multiple emails at once, and LINK offers predictive filing by recommending folders. Filing attachments to your DMS is just as easy. LINK syncs with your Outlook email, calendars, contacts, notes, and tasks, making for seamless workflows.
Security
On top of everything else, LINK incorporates all the security features you need for the peace of mind that you’re working with and sending your documents safely. Its robust security features include Face ID authentication, a secure container app, and encryption, to name just a few.
Put simply, LINK’s security has been vetted by Am Law 100 firms and has been penetration-tested by an outside consulting firm, so you can use it without worrying that you’re compromising any sensitive or confidential information.
LINK: The Future of Better Work
Your mobile devices go everywhere you go, and they should work the way you work. With LINK, they do.
Gone are the days when documents threw a wrench in your ability to work on the go. LINK offers the single-app workflows you need to fully work on your documents and manage your email from your mobile devices, anytime and anywhere.
If you want document workflows that really work on your phone or tablet, you need LINK.
Apps in Law, Legal Services, Legal Technology, LINK, Software, Sponsored Content, Stephanie Wilkins, Technology
We will never sell or share your information without your consent. See our privacy policy.
Our Sites
© 2022 Breaking Media, Inc. All rights reserved. Registration or use of this site constitutes acceptance of our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Privacy Center | Do not sell my information

- Published in Uncategorized
What Is Data Management, and How Do Businesses Use It? – business.com – Business.com
business.com receives compensation from some of the companies listed on this page. Advertising Disclosure
Most modern businesses recognize the value of data, and for small businesses, this often means relying on reports generated within the individual software platforms they use for daily operations. However, there comes a time when unifying this data in a central, standardized source is desirable. To effectively organize and secure this data requires a process known as data management.
Data management is the process by which businesses gather, store, access and secure data from various business software solutions. Employing data management enables more efficient access to data analytics that offer insights that are needed to improve business operations and identify opportunities for improvement. By establishing a better framework to access the wide swaths of data that every business generates, companies can make more informed decisions and improve their ability to deliver valuable products and services to their customers.
“Data management involves multiple disparate functions and systems working together to move, organize, and secure data such that it is accurate, precise, accessible and protected,” said Christopher Risher, senior program manager of application management services at Onepath.
In a modern business environment, virtually every piece of software collects data. These include accounting software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, point of sale software, credit card processing software and more. These systems feed a wide variety of data into the business, including customer data, financial data and more.
“Nowadays every company has data, from the multinational giants of IT to the small local breweries. Some data are sensitive, some are history, some can be used for future predictions, some for auditing, and so on,” said Rosaria Silipo, principal data scientist at KNIME. “With so much data and so many different properties and usages, a different set of rules and competences is required to handle each subset of data. You can see then that data management can quickly become a quite complex and tricky task, which can bring further prosperity or further problems to the company.”
As the number of business software platforms proliferate, so too does a business’s ability to gather data and employ data analytics to derive key insights from it. However, organizing that data in a centralized system can sometimes be challenging. Developing a data management strategy is a must for businesses that want to maintain a competitive advantage and improve both customer-facing and internal elements of business operations.
To begin implementing a data management policy, businesses need to understand the tools available to them to do so.
“Managing data typically begins with a project that’ll get started in one of the knowledge areas and iterate through the other knowledge areas,” Risher said. “Utilizing cloud-enabled tools can assist in the rapid development of a data management platform. These cloud tools can empower an organization regardless of the location of their data.”
In addition, data management should serve to standardized data in a way that makes it effective for business purposes. Not every software platform will collect data in the same way, or even collect the same types of data. Data management serves to unify these data silos so they become useful when combined.
“Organizations are dealing with more data from more sources than ever before (known as big data). They have come to realize that all this data can provide a wealth of new insights into customer buying behavior and the dynamics of their industry – but only if this data is managed and trusted,” said Todd Wright, head of data management solutions at SAS.
How data is managed directly relates to data quality, which must be unassailable if any data analytics efforts are to bear fruit. Decisions made based on faulty data will in turn be faulty decisions, so data quality should be of the utmost importance to any business relying on this information.
Data management systems make the process of data management more manageable, automating some of the most arduous aspects of unifying and reviewing key data. These systems incorporate databases and analytics tools that allow businesses to not only store and organize important data but also query the system as needed. The best systems consolidate data into useful reports that include visualizations that provide the ability to contextualize data at a glance. Some even incorporate automated decision-making recommendations empowered by machine learning, helping key stakeholders make more informed, effective choices about how to govern the business’s operations.
Some examples of data management systems include:
“The goal of data management is to give an organization reliable and quickly accessible data through which decisive action can be taken in a secure manner,” Risher said.
These data management systems are crucial tools to achieve that goal, especially as the amount of data collected by businesses becomes too vast for any human to contextualize manually. Data management systems are required to make sense of the overwhelming amount of data most businesses generate.
When developing a data management strategy, you should start by understanding your key business objectives. Make a list of these objectives and then identify what data you are already collecting that is relevant to each objective, noting any overlap between objectives or gaps in the data you already maintain. Once you have established a comprehensive list, ask yourself what is the best way in which to organize and secure this data for later retrieval.
“From a strategy perspective, data management and its underlying knowledge areas provide a construct to give analytical data models what is needed to receive reliable insights,” Risher said. “Without proper implementation of data management controls, some level of the pipeline that feeds an analytical data model can be rendered unreliable. If we are basing strategic, forward-thinking decisions off poorly gathered data, then we are likely impacting the business by making incorrect decisions.”
To better structure the vast troves of data generated by a company on any given day, it is important to tie that data to your specific business objectives. Not only will these objectives guide the collection and organization of data, it also makes clear who should be able to access that data, and when and why.
“When we take ownership of the data in the company, we need to make sure we understand their position in the bigger strategy. Based on their role and features, we need to define a sub-strategy for protection, storage, and usage,” Silipo said. “A successful data management strategy allocates a place, a task, and a policy to each subset of the data, in terms of privacy, storage, and usage.”
A data management strategy must incorporate multiple goals, including the ability to audit business operations, monitor progress toward organizational goals, and gain insight into what is working and what is not. Each of these goals requires a different approach to data management, meaning your systems and policies must be flexible enough to address each while being standardized enough to offer suitable levels of security and restrict access to key stakeholders who need to access the data most.
“Depending on the goal, you need a different tool to manage a different subset of data: from classic databases to highly secure data repositories, from data visualization tools to more advanced data analysis tools,” Silipo said.
These data management best practices can improve your organization’s relationship with the data it collects and stores, making it easily accessible for use in improving business processes, as well as ensuring collection and usage comply with laws and regulations and up to current security standards.
Data management is a vast and complex area of business operations. That means it requires a knowledgeable and dedicated team of data management professionals to manage it correctly. Few small business owners are capable of giving data management processes the time and attention they deserve, even if they have a background in data themselves. Hiring a data management professional team with the depth and breadth of knowledge to do so is an absolute must.
“First of all, you need to have a global vision of the data strategy in your company, to make sure that all pieces of information are recorded and all are exploited to generate more insights into the company process and business,” Silipo said.
An experienced and skilled team with advanced data management skills is crucial to developing and refining a global approach to data management. Rely on your team, whether in-house or outsourced, to act not just as managers but consultants when it comes to connecting your business’s data to its wider operations.
This team should be equipped with user-friendly tools to monitor, access, and organize data, both while it is stored and as it is collected. Employing some of the data management systems mentioned above should be a top priority alongside hiring the right team.
As data privacy laws become increasingly common – such as the EU’s GDPR or California’s CCPA – data privacy compliance is critical. Not only should your data management plan be useful for your business operations, it must also be auditable in a way that easily demonstrates compliance to regulators and business partners.
“You need to know how each subset of data must be protected, stored, and analyzed depending on its nature and on its strategic importance,” Silipo said. “Here a number of skills are joined together: legal skills to design the rules, IT skills to see the implementation of the rules, programming skills to retrieve the data, and some statistics and data analysis to understand how these data can become useful.”
As any cybersecurity professional will tell you, the threat landscape is constantly changing, and malicious actors are becoming more sophisticated in the way they infiltrate systems. Small businesses are prime targets, because hackers know they are typically less protected than large enterprises. As a result, small business owners must regularly revisit their security policies and revise them to meet the threats of the day. This includes giving your IT team the ability to monitor for and respond to new threats as they emerge, taking a proactive approach to the protection of your centralized data.
“Security is always top of mind. So, having access to a security professional, such as a CISO to validate the security parameters is extremely valuable,” Risher said.
megaflopp / Getty Images
- Published in Uncategorized
How To Create E-Learning Modules That Boost Training Retention – Software Advice
For free software advice, call us now! 855-998-8505
By: Sierra Rogers on September 28, 2022
In early 2022, Software Advice polled nearly 300 HR leaders for the Toxic Culture Survey[*] and found that nearly half (49%) are spending more than they have previously on upskilling employees in 2022. However, despite the increase in resources devoted to training initiatives, organizations are struggling to create engaging, effective training modules.
At least, that’s what employees are saying: Recent research from Gartner revealed that more than 40% of employees report that the compliance and ethics training they received in the past 12 months did not help them perform their job better[1].
Obviously, this is not the outcome that employees that are responsible for developing training programs are hoping for. But the reality is that if you want to create more memorable training programs, you’re going to need to go beyond the basics and start incorporating advanced e-learning elements into your training modules.
So, if you’re a corporate trainer or team manager who’s taken on the task of leveling up your current training modules, say goodbye to hastily slapped together slide decks, because we’ve laid out a step-by-step process for creating effective e-learning training modules.
Follow the five steps outlined below to start building e-learning modules that improve training retention.
Before you begin the process of creating training content, you need to determine what it is you want your employees to take away from the module you’re building. Is it a concept, a set of best practices, or a new process they’ll be learning? Depending on the answer, how you format your training module will be different.
According to Ebbinghaus’s Forgetting Curve, people forget an average of 50% of new information they’re presented with within an hour and 90% within a week[2]. Knowing this, we suggest keeping your training modules short and focused (rather than trying to provide as much information as possible on a topic). This may mean breaking down a larger training objective into smaller milestones.
For example, let’s say that you’re working on creating an e-learning module that will help prepare a new sales representative for their first call with a lead.
In this scenario, the goal of your module could be for the rep to master the sales script your organization follows. Or, the goal could be to teach the rep how to research the lead they’re calling and tailor their pitch to their background.
Either way, the idea is to be specific about the training objective your module is targeting and to not cram too much information into one e-learning module.
One benefit of using an e-learning tool or learning management system to create training modules is that there’s a whole wide world of content formats available to you. With that level of possibility at your fingertips, knowing which content formats to use (and when) to get a point across is essential in order to boost your employees’ knowledge retention.
Below, we’ve provided you with a cheat sheet that gives an overview of seven common types of e-learning content formats and what they’re best used for.
Use this table to determine what content format(s) your module should include, and to avoid overloading trainees, stick to two or three content formats per module.
Continuing with our example from the first step, if your goal is to help a new hire master your company’s sales script, you could first show a video of two employees running through the script, then have new hires reinforce what they’ve learned through roleplay (social learning) with another employee or through an e-learning simulation.

A roleplay scenario used to train customer service representatives in Day One[3]
Once you’ve determined what your content will cover and how you will present it, it’s time to start creating your e-learning modules.

A dropdown menu shows content format options in TalentLMS (Source)
Building modules is a responsibility that should be divided between HR professionals and team managers. For instance, if the module is a compliance training, a corporate trainer should be the one to develop it, but if it’s team-specific (such as introducing a new project workflow), then a leader from that team should take the reins. All this to say, make sure that your course authoring tool of choice allows for multiple individuals to be assigned an admin role so that the task of creating training is easy to manage.
Lastly, before you begin, have a quick brainstorming session, and map out the contents of your module in a data management tool, such as a Microsoft Word document or a spreadsheet. Keep this step simple: Write down the information you plan to share with the learner and the content formats you’ll use to accomplish that. That way, you’ll have a reference you can turn to when you begin building your module in your course authoring tool.
Now that you’ve built your module, all that’s left to do is follow a few steps to ensure that employees know how to access it and by what date they’re expected to complete it. Follow the four tips below for a successful training rollout to your workforce or team:

A manager dashboard shows completion and participation rates in 360Learning (Source)
Lastly, in order to prevent the concepts or practices presented in your training module from becoming long forgotten, you need to provide a chance for your employees to use what they’ve learned. Without doing so, the new information they’ve taken in will fade away, and the work you put into building the training will have been a waste of effort.
For example, if you watch a YouTube tutorial on how to bake a soufflé, but then you never pull out a ramekin or beat an egg white, the chances are low that you’ll remember the specific set of instructions you’re supposed to follow.
So what does this look like in a professional setting? The truth is that it will be different depending on the subject of your training, but here are a few examples of how this step could play out:
As someone who’s in charge of developing training programs for your organization, think about how the contents of each module you create will be applied in the workplace. Then, once a training module has been developed, look ahead a few weeks and plan an opportunity for employees to apply what they’ve learned.
In this guide, we’ve covered five steps for creating engaging, retainable employee training modules:

Following these steps will ensure that the content in your e-learning modules is focused and engaging, and that your training strategy is built with knowledge retention as a top priority.
Our final piece of advice is this: Adjust your training as necessary based on your employees’ performance and feedback.
As we mentioned in the fourth step of this process (plan for a successful deployment), most learning management systems have reporting functions. Use this feature to track your employees’ engagement with training modules, and ultimately, determine if your e-learning strategy is successful.

A reporting dashboard in Looop shows learners’ activity time and resource views over the course of a year (Source)
As far as acquiring employees’ feedback goes, you have a few options. You can encourage managers to request feedback from their team members in one-on-ones, send a survey out via a survey tool, or take advantage of your LMS’s assessment feature by incorporating an optional feedback form at the end of each module you develop. Whatever method you choose, look for patterns in the feedback from employees and adjust your e-learning strategy as necessary.
The majority (86%) of businesses that increased their L&D budget for 2022 say they plan to spend more on learning and training technology[*]. Join your peers; connect with an advisor to find a learning management system that works for your organization today.
Sources
Survey methodology
*Software Advice’s 2022 Toxic Culture Survey was conducted in January 2022 among 294 HR leaders at U.S. companies. An HR leader is defined as any HR employee with the role of HR manager or higher at their organization. The goal of this survey was to learn how the transition to hybrid and remote work impacted toxic employee behaviors.
Note: The applications mentioned in this article are examples to show a feature in context and are not intended as endorsements or recommendations. They have been obtained from sources believed to be reliable at the time of publication.
5 Ways LMSs Can Improve Employee Knowledge Retention
5 Best E-learning Content Authoring Tools for Corporate Trainers
Filling the 5 Biggest Gaps in Your LMS Business Case
© 2006-2022 Software Advice, Inc. TermsPrivacy PolicyCommunity GuidelinesGeneral Vendor TermsGDM Content PolicyGDM Content Policy FAQs
- Published in Uncategorized
Microsoft: Watch out for password spray attacks – especially you, Basic Auth – The Register
- Published in Uncategorized
Applications for artificial intelligence in Department of Defense cyber missions – Microsoft On the Issues – Microsoft
May 3, 2022 Microsoft Corporate Blogs
Editor’s note: On May 3 Eric Horvitz, Chief Scientific Officer, testified before the U.S. Senate Armed Services Committee Subcommittee on Cybersecurity for a hearing on the use of AI in Department of Defense cyber missions. Read Eric Horvitz’s written testimony below and watch the hearing here.
Chairman Manchin, Ranking Member Rounds, and Members of the Subcommittee, thank you for the opportunity to share insights about the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on cybersecurity. I applaud the Subcommittee for its foresight and leadership in holding a hearing on this critically important topic. Microsoft is committed to working collaboratively with you to help ensure new advances in AI and cybersecurity benefit our country and society more broadly.
My perspective is grounded in my experiences working across industry, academia, scientific agencies, and government. As Microsoft’s Chief Scientific Officer, I provide leadership and perspectives on scientific advances and trends at the frontiers of our understandings, and on issues and opportunities rising at the intersection of technology, people, and society. I have been pursuing and managing research on principles and applications of AI technologies for several decades, starting with my doctoral work at Stanford University. I served as a Commissioner on the National Security Commission on AI (NSCAI), was president of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), chaired the Section on Computing, Information, and Communication of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). I am a member of the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. I currently serve on the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST) and on the Computer Science and Telecommunications Board (CSTB) of the National Academies of Sciences.
I will cover in my testimony four key areas of attention at the intersection of AI and cybersecurity that warrant deeper understanding and thoughtful action:
Before covering these topics, I will provide brief updates on the cybersecurity landscape and on recent progress in AI. I’ll conclude my testimony with reflections about directions.
1. Cybersecurity’s changing landscape
Attacks on computing systems and infrastructure continue to grow in complexity, speed, frequency, and scale. We have seen new attack techniques and the exploitation of new attack surfaces aimed at disrupting critical infrastructure and accessing confidential data.[1] In 2021 alone, the Microsoft 365 Defender suite, supported by AI techniques, blocked more than 9.6 billion malware threats, 35.7 billion phishing and malicious emails, and 25.6 billion attempts to hijack customer accounts targeting both enterprise and consumer devices.[2],[3] Multiple independent reports have characterized the nature and status of different forms of cyberattack.[4] As detailed in Microsoft’s recent Digital Defense Report,[5] cyber criminals and nation-state actors continue to adapt their techniques to exploit new vulnerabilities and counter cyber defenses.
To help mitigate these concerning trends, the U.S. government has taken significant steps forward to secure our cyber ecosystem. Congress enacted several recommendations that came out of the Cyberspace Solarium Commission, such as creating the Office of the National Cyber Director and enacting cyber incident reporting legislation. Almost a year ago, the Administration issued Executive Order (E.O.) 14028, Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity, which directs agencies to develop and implement a variety of initiatives to raise the bar on cybersecurity across areas, such as supply chain security, and requiring agencies to adopt a zero-trust model. Microsoft has worked diligently to meet deadlines specified in the E.O. on cybersecurity and we support these efforts to encourage a cohesive response to evolving cyber threats.
We expect to face continuing efforts by creative and tireless state and non-state actors who will attempt to attack computing systems with the latest available technologies. We need to continue to work proactively and reactively to address threats and to note changes in systems, technologies, and patterns of usage. On the latter, cybersecurity challenges have been exacerbated by the increasing fluidity between online work and personal activities as daily routines have become more intertwined.[6] The large-scale shift to a paradigm of hybrid work coming with the COVID-19 pandemic has moved workers further away from traditional, controlled environments. Cybersecurity solutions must enable people to work productively and securely across various devices from a variety of non-traditional locations.
2. Advancements in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is an area of computer science focused on developing principles and mechanisms to solve tasks that are typically associated with human cognition, such as perception, reasoning, language, and learning. Numerous milestones have been achieved in AI theory and applications over the 67 years since the phrase “artificial intelligence” was first used in a funding proposal that laid out a surprisingly modern vision for the field.[7]
Particularly stunning progress has been made over the last decade, spanning advances in machine vision (e.g., object recognition), natural language understanding, speech recognition, automated diagnosis, reasoning, robotics, and machine learning—procedures for learning from data. Many impressive gains across subdisciplines of AI are attributed to a machine learning methodology named deep neural networks (DNNs). DNNs have delivered unprecedented accuracy when fueled by large amounts of data and computational resources.
Breakthroughs in accuracy include performances that exceed human baselines for a number of specific benchmarks, including sets of skills across vision and language subtasks. While AI scientists remain mystified by the powers of human intellect, the rate of progress has surprised even seasoned experts.
Jumps in core AI capabilities have led to impressive demonstrations and real-world applications, including systems designed to advise decision makers, generate textual and visual content, and to provide new forms of automation, such as the control of autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles.
AI technologies can be harnessed to inject new efficiencies and efficacies into existing workflows and processes. The methods also can be used to introduce fundamentally new approaches to standing challenges. When deployed in a responsible and insightful manner, AI technologies can enhance the quality of the lives of our citizenry and add to the vibrancy of our nation and world. For example, AI technologies show great promise in enhancing healthcare via providing physicians with assistance on diagnostic challenges, guidance on optimizing therapies, and inferences about the structure and interaction of proteins that lead to new medications.
AI advances have important implications for the Department of Defense, our intelligence community, and our national security more broadly. Like any technology, the rising capabilities of AI are available to friends and foes alike. Thus, in addition to harnessing AI for making valuable contributions to people and society, we must continue to work to understand and address the possibilities that the technologies can be used by malevolent actors and adversaries to disrupt, interfere, and destroy. AI has important implications for cybersecurity as the technologies can provide both new powers for defending against cyberattacks and new capabilities to adversaries.
3. Advancing Cybersecurity with AI
The value of harnessing AI in cybersecurity applications is becoming increasingly clear. Amongst many capabilities, AI technologies can provide automated interpretation of signals generated during attacks, effective threat incident prioritization, and adaptive responses to address the speed and scale of adversarial actions. The methods show great promise for swiftly analyzing and correlating patterns across billions of data points to track down a wide variety of cyber threats of the order of seconds. Additionally, AI can continually learn and adapt to new attack patterns—drawing insights from past observations to detect similar attacks that occur in the future.
3.1 Assisting and Complementing Workforce
The power of automation and large-scale detection, prioritization, and response made possible by AI technologies can not only relieve the burden on cybersecurity professionals but also help with the growing workforce gap. On the challenges to current cyber workforce: the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates cybersecurity job opportunities will grow 33% from 2020 to 2030—more than six times the national average.[8] However, the number of people entering the field is not keeping pace. There is a global shortage of 2.72 million cybersecurity professionals, according to the 2021 (ISC)2 Cybersecurity Workforce Study released in October 2021.[9]
Organizations that prioritize cybersecurity run security operations teams 24/7. Still, there are often far more alerts to analyze than there are analysts to triage them, resulting in missed alerts that evolve into breaches. Trend Micro released a survey in May 2021 of security operations center decision makers that showed that 51% feel their team is overwhelmed with the overall volume of alerts, 55% are not confident in their ability to efficiently prioritize and respond to alerts, and that 27% of their time is spent dealing with false positives.[10]
AI technologies enable defenders to effectively scale their protection capabilities, orchestrate and automate time-consuming, repetitive, and complicated response actions. These methods can enable cybersecurity teams to handle large volumes of classical threats in more relevant time frames with less human intervention and better results. Such support with scaling on the essentials can free cybersecurity professionals to focus and prioritize on those attacks that require specialized expertise, critical thinking, and creative problem solving. However, additional attention should also be given to general cybersecurity training, security awareness, secure development lifecycle practices, and simulated training modules, including using AI to run intelligent and personalized simulations.
3.2 AI at Multiple Stages of Security
Today, AI methods are being harnessed across all stages of security including prevention, detection, investigation and remediation, discovery and classification, threat intelligence, and security training and simulations. I will discuss each of these applications in turn.
Prevention. Prevention encompasses efforts to reduce the vulnerability of software to attack, including user identities and data, computing system endpoints, and cloud applications. AI methods are currently used in commercially available technologies to detect and block both known and previously unknown threats before they can cause harm. In 2021, AV-Test Institute observed over 125 million new malware threats.[11] The ability of machine learning techniques to generalize from past patterns to catch new malware variants is key to being able to protect users at scale.
As an example, last year Microsoft 365 Defender successfully blocked a file that would later be confirmed as a variant of the GoldMax malware. Defender had never seen the new variant of GoldMax. The malware was caught and blocked leveraging the power of an AI pattern recognizer working together with a technology known as “fuzzy hashing”—a means for taking a fingerprint of malware.[12] It is important to note that GoldMax is malware that persists on networks, feigning to be a “scheduled task” by impersonating the activities of systems management software. Such hiding out as a scheduled task is part of the tools, tactics, and procedures of NOBELIUM, the Russian state actor behind the attacks against SolarWinds in December 2020 and which the U.S. government and others have identified as being part of Russia’s foreign intelligence service known as the SVR.
In other work, we have found that AI methods can improve our ability to detect sophisticated phishing attacks. Phishing attacks center on social engineering, where an attacker creates a fake webpage or sends a fraudulent message designed to trick a person into revealing sensitive data to the attacker or to deploy malicious software on the victim’s device, such as ransomware. To help protect people from harmful URLs, AI pattern recognizers have been deployed in browsers and other applications as part of their security services. AI methods can improve detection while lowering false positive rates, which can frustrate end users.[13]
Detection. Detection involves identifying and alerting suspicious behaviors as they happen. The goal is to quickly respond to attacks, including identifying the scale and scope of an attack, closing the attacker’s entry, and remediating footholds that the attacker may have established. The key challenge with detecting suspicious activity is to find the right balance between providing enough coverage via seeking high rates of accurate security alerts versus false alarms. AI methods are being leveraged in detection to (1) triage attention to alerts about potential attacks, (2) identify multiple attempts at breaches over time that are part of larger and lengthier attack campaigns, (3) detecting fingerprints of the activities of malware as it operates within a computer or on a network, (4) identifying the flow of malware through an organization,[14] and (5) guiding automated approaches to mitigation when a response needs to be fast to stop an attack from propagating. For example, an automated system can shut down network connectivity and contain a device if a sequence of alerts is detected that is known to be associated with ransomware activity like the way a bank might decline a credit card transaction that appears fraudulent.
There are several technologies available today to help detect attacks. I will use Microsoft 365 Defender capabilities as an example. A set of neural network models are used to detect a potential attack underway by fusing multiple signals about activities within a computing system, including processes being started and stopped, files being changed and renamed, and suspicious network communication.[15], [16] In addition, probabilistic algorithms are used to detect high likelihoods of “lateral movement” on a network.[17] Lateral movement refers to malware, such as ransomware, moving from machine to machine as it infects an organization. The goal is to detect signals of concerning patterns of spread and to shut down the infection by isolating potentially infected machines and alerting security experts to investigate. As numerous legitimate operations can appear like lateral movement of malware, simplistic approaches can have high false-positive rates. AI systems can help to raise the rate of capture and block these spreading infections, while reducing false positives.[18]
As a recent example, in March 2022, Microsoft leveraged its AI models to identify an attack attributed to a Russian actor that Microsoft tracks as Iridium, also referred to as Sandworm. The US government has attributed Iridium activity to a group allegedly based at GRU Unit 74455 of the Main Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. The actor deployed wiper malware at a Ukrainian shipping company based in Lviv. Wiper malware erases data and programs on the computers that it infects. The first documented encounter of this malware was on a system running Microsoft Defender with Cloud Protection enabled. The ensemble of machine learning models in Defender, combined with signals across client and cloud, allowed Microsoft to block this malware at first sight.
Investigation and remediation. Investigation and remediation are methods used following a breach to provide customers with a holistic understanding of the security incident, including the extent of the breach, which devices and data were impacted, how the attack propagated through the customer environment, and to seek attribution for the threat.[19] Gathering and doing synthesis from telemetry sources is tedious. Efforts to date include multiple tools to collect telemetry from within and across organizations. The use of AI for investigation and remediation is a promising and open area of research.[20],[21]
Threat intelligence. Threat intelligence enables security researchers to stay on top of the current threat landscape by tracking active malicious actors, at times deliberately engaging with them and studying their behavior. Today, Microsoft actively tracks 40+ active nation-state actors and 140+ threat groups across 20 countries.[22],[23] AI methods help to identify and tag entities from multiple feeds and intelligence sharing across agencies. AI models show promise with their ability to learn and make inferences about high-level relationships and interactions by identifying similarities across different campaigns for enhancing threat attribution.[24],[25]
Recommendations: Advance development and application of AI methods to defend against cyberattacks
4. AI-powered cyberattacks
While AI is improving our ability to detect cybersecurity threats, organizations and consumers will face new challenges as cybersecurity attacks increase in sophistication. To date, adversaries have commonly employed software tools in a manual manner to reach their objectives. They have been successful in exfiltrating sensitive data about American citizens, interfering with elections, and distributing propaganda on social media without the sophisticated use of AI technologies. [26],[27],[28] While there is scarce information to date on the active use of AI in cyberattacks, it is widely accepted that AI technologies can be used to scale cyberattacks via various forms of probing and automation. Multiple research and gaming efforts within cybersecurity communities have demonstrated the power using AI methods to attack computing systems. This area of work is referred to as offensive AI.[29],[30]
4.1 Approaches to offensive AI
Offensive AI methods will likely be taken up as tools of the trade for powering and scaling cyberattacks. We must prepare ourselves for adversaries who will exploit AI methods to increase the coverage of attacks, the speed of attacks, and the likelihood of successful outcomes. We expect that uses of AI in cyberattacks will start with sophisticated actors but will rapidly expand to the broader ecosystem via increasing levels of cooperation and commercialization of their tools.[31]
Basic automation. Just as defenders use AI to automate their processes, so too can adversaries introduce efficiencies and efficacies for their own benefit. Automating attacks using basic pre-programmed logic is not new in cybersecurity. Many malware and ransomware variants over the last five years have used relatively simple sets of logical rules to recognize and adapt to operating environments. For example, it appears that attacking software has checked time zones to adapt to local working hours and customized behavior in a variety of ways to avoid detection or take tailored actions to adapt to the target computing environment.[32],[33] On another front, automated bots have begun to proliferate on social media platforms.[34] These are all rudimentary forms of AI that encode and harness an attacker’s expert knowledge. However, substantial improvements in AI technology make plausible malicious software that is much more adaptive, stealthy, and intrusive.[35]
Authentication-based attacks. AI methods can be employed in authentication-based attacks, where, for example, recently developed AI methods can be used to generate synthetic voiceprints to gain access through an authentication system. Compelling demonstrations of voice impersonations to fool an authentication system were presented during the Capture the Flag (CTF) cybersecurity competition at the 2018 DEF CON meeting.[36]
AI-powered social engineering. Human perception and psychology are weak links in cyber-defense. AI can be used to exploit this persistent vulnerability. We have seen the rise of uses of AI for social engineering, aiming the power of machine learning at influencing the actions of people to perform tasks that are not in their interest. As an example, AI methods can be used to generate ultra-personalized phishing attacks capable of fooling even the most security conscious users. A striking 2018 study demonstrated how AI methods could be used to significantly raise the probability that end users would click on malevolent links in social media posts. The AI system learned from publicly available data including online profiles, connections, content of posts, and online activity of targeted individuals. Machine-learning was used to optimize the timing and content of messages with a goal of maximizing clickthrough rates—with significant results.[37] A 2021 study demonstrated that the language of emails could be crafted automatically with large-scale neural language models and that the AI-generated messages were more successful than the human-written messages by a significant margin.[38] In a related direction, Microsoft has tracked groups that use AI to craft convincing but fake social media profiles as lures.
4.2 AI-powered cyberattacks on the frontier
The need to prepare for more sophisticated offensive AI was highlighted in presentations at a National Academies of Sciences workshop on offensive AI that I co-organized in 2019. The workshop, sponsored by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence, led to a report available from the Academies.[39] The report includes discussion of the applications of AI methods across the cyber kill-chain, including the use of AI methods in social engineering, discovery of vulnerabilities, exploiting development and targeting, and malware adaptation, as well as in methods and tools that can be used to target vulnerabilities in Al-enabled systems, such as autonomous systems and controls used in civilian and military applications.
The cybersecurity research community has demonstrated the power of AI and other sophisticated computational methods in cyberattacks. Adversaries can harness AI to efficiently guess passwords, to attack industrial control systems without raising suspicions, and to create malware that evades detection or prevents inspection[40],[41],[42],[43],[44],[45] AI-enabled bots can also automate network attacks and make it difficult to extinguish the attacker’s command and control channels.[46] In another direction, a competitor demonstrated at a DARPA Cyber Grand Challenge exercise in 2016 [47] how machine learning could be used to learn how to generate “chaff” traffic, decoy patterns of online activity that resemble the distribution of events seen in real attacks for distraction and cover-up of actual attack strategies.[48]
It is safe to assume that AI will improve the success, impact, and scope of the full breadth of threats present today. AI will also introduce new challenges, including special cyber vulnerabilities introduced with general uses of AI components and applications, which create new apertures for adversaries to exploit.
Recommendations: Prepare for malicious uses of AI to perform cyberattacks
5. Special vulnerabilities of AI systems
The power and growing reliance on AI generates a perfect storm for a new type of cyber-vulnerability: attacks targeted directly at AI systems and components. With attention focused on developing and integrating AI capabilities into applications and workflows, the security of AI systems themselves is often overlooked. However, adversaries see the rise of new AI attack surfaces growing in diversity and ubiquity and will no doubt be pursuing vulnerabilities. Attacks on AI systems can come in the form of traditional vulnerabilities, via basic manipulations and probes, and via a new, troubling category: adversarial AI.
5.1 Attacks on AI Supply Chains
AI systems can be attacked via targeting traditional security weaknesses and software flaws, including attacks on the supply chain of AI systems, where malevolent actors gain access and manipulate insecure AI code and data. As an example, in 2021, a popular software platform used to build neural networks was found to have 201 traditional security vulnerabilities, such as memory corruption and code execution.[50] Researchers have demonstrated how adversaries could use existing cyberattack toolkits to attack core infrastructure of the software running AI systems.[51] Multiple components of AI systems in the supply chain of AI systems can be modified or corrupted via traditional cyberattacks. As an example, data sets used to train AI systems are rarely under version control in the same way that source code is. Researchers from NYU found that most AI frameworks downloaded from a popular algorithm repository do not check the integrity of AI models, in contrast to the standards of practice with traditional software, where cryptographic verification of executables/libraries has been standard practice for well over a decade.[52]
5.2 Adversarial AI
Adversarial AI or adversarial machine learning methods harness more sophisticated AI techniques to attack AI systems. Several classes of adversarial AI have been identified, including adversarial examples, the use of basic policies or more sophisticated machine learning methods to fool AI systems with inputs that cause the systems to fail to function properly. A second type of attack is called data poisoning, where data used to train AI systems are “poisoned” with streams of data that inject erroneous or biased training data into data sets, changing the behavior or degrading the performance of AI systems.[53] A third type of attack, called model stealing, seeks to learn details about the underlying AI model used in an AI system.[54] A fourth category of attack, called model inversion, seeks to reconstruct the underlying private data that is used to train the target system.[55]
With adversarial examples, basic manipulations or more sophisticated application of AI methods are used to generate inputs that are custom-tailored to cause failures in targeted AI systems. Goals of these attacks include disruptive failures of automated message classifiers, perceptions of machine vision systems, and recognitions of the words in utterances by speech recognition systems.
As an example of basic manipulations of inputs, a group, alleged to be within the Chinese government, attempted to amplify propaganda on Uyghurs by bypassing Twitter’s anti-spam algorithm via appending random characters at the end of tweets.[56] The approach was viewed as an attempt to mislead the algorithm into thinking each tweet was unique and legitimate. In another example, researchers from Skylight appended benign code from a gaming database to Wannacry ransomware to cause the machine-learning-based antivirus filter to classify the modified ransomware as benign.[57] In related work on the fragility of AI systems, researchers showed that simply rotating a scan of a skin lesion confuses a computer recognition system to classify the image as malignant.[58]
In uses of AI to generate adversarial examples, researchers have demonstrated stunning examples of failures. In one approach, adversarial methods are used to inject patterns of pixels into images to change what an AI system sees. While the changes with AI inferences are dramatic, the changes to the original images are not detectable by humans. Sample demonstrations include the modification of a photo of a panda leading an AI system to misclassify the panda as a gibbon and changes to a stop sign to misclassify it as a yield sign.[59],[60] Similar demonstrations have been done in the realm of speech recognition, with the injection of hidden acoustical patterns in speech that changes what a listening system hears.[61] Attacks leading to such misclassifications and malfunctions can be extremely costly, particularly in high-stakes domains like defense, transportation, healthcare, and industrial processes.
Challenges of adversarial AI and a set of recommendations are called out in the final report of the National Security Commission on AI (NSCAI).[62] I chaired the lines of effort on directions with developing and fielding trustworthy, responsible, and ethical AI applications, leading to chapters 7 and 8 of the report and the appendix on NSCAI’s recommendations on key considerations for fielding AI systems that align with democratic values, civil liberties, and human rights.[63],[64],[65] Chapter 7 of the report covers rising concerns with adversarial AI, including the assessment that, “The threat is not hypothetical: adversarial attacks are happening and already impacting commercial ML systems.” In support of this statement, over the last five years, the Microsoft cybersecurity team has seen an uptick in adversarial AI attacks.[66] I believe the trend will continue.
5.3 Efforts to Mitigate Adversarial AI
Pursuit of resistant systems. Computer science R&D has been underway on methods for making AI systems more resistant to adversarial machine learning attacks. One area of work centers on raising the level of robustness of systems to attacks with adversarial inputs as described above.[67],[68] Approaches include special training procedures to include adversarial examples, validation of inputs to identify specific properties that can reveal signs of an attack and making changes to the overall approach to building models, and modifying the objective functions used in optimization procedures used to create the models so that more robust models are created. While the latter techniques and research directions behind them are promising, the challenges of adversarial examples persist, per the large space of inputs to machine learning procedures. Thus, it is important to continue to invest in R&D on adversarial AI, to perform ongoing studies with red-teaming exercises, and to remain vigilant.
5.4 Tracking, Awareness, and Resources
Front-line awareness. Despite the opportunities that adversarial AI methods will provide to state and non-state actors for manipulating and disrupting critical AI systems and rising evidence of real-world attacks with adversarial AI, the idea of protecting AI systems from these attacks has been largely an afterthought. There is an urgency to be aware and to be ready to respond to adversarial AI threats, especially those used in critical areas such as defense. A Microsoft survey of 28 organizations in 2020 showed, despite the rise in attacks on AI systems, companies are still unaware of these kinds of intentional failures to AI systems and are massively underinvested in tools and processes to secure AI systems. Ryan Fedasiuk, a noted researcher at Georgetown’s Center for Security of Emerging Technology specializing in China’s AI operations, notes that Chinese military officers have explicitly called out that the U.S. defenses are susceptible to data poisoning, and even so far as calling data integrity as “the Achilles’ heel” of the U.S. joint all-domain command and control strategy.[69]
Resources and Engagement. Microsoft, along with MITRE and 16 other organizations created the Adversarial ML Threat Matrix to catalog threats to AI systems.[70] The content includes documentation of case studies where attacks have been made on commercial AI systems. For engineers and policymakers, Microsoft, in collaboration with Berkman Klein Center at Harvard University, released a taxonomy of machine learning failure modes.[71] For security professionals, Microsoft has open-sourced Counterfit, its own tool for assessing the posture of AI systems.[72] For the broader community of cybersecurity practitioners interested in AI and security, Microsoft hosts the annual Machine Learning Evasion Competition as a venue to exercise their muscle in attacking and securing AI systems.[73] Within the Federal government, the DoD has listed safety and security of AI systems in its core AI principles.[74] And there is encouraging activity by NIST on an AI Risk Assessment Framework to address multiple dimensions of AI systems, including robustness and security.[75]
Recommendations: Raise awareness and address vulnerabilities of AI systems
6. AI in Malign Information Operations
Advances in machine learning and graphics have boosted the abilities of state and non-state actors to fabricate and distribute high-fidelity audiovisual content, referred to as synthetic media and deepfakes. AI technologies for generating deepfakes can now fabricate content that is indistinguishable from real-world people, scenes, and events, threatening national security. Advances that could only be found with the walls of computer science laboratories or in demonstrations that surprised attendees at academic AI conferences several years ago are now widely available in tools that create audio and audiovisual content that can be used to drive disinformation campaigns.
6.1 Challenges of Synthetic Media
Advances in the capabilities of generative AI methods to synthesize a variety of signals, including high-fidelity audiovisual imagery, have significance for cybersecurity. When personalized, the use of AI to generate deepfakes can raise the effectiveness of social-engineering operations (discussed above) in persuading end-users to provide adversaries with access to systems and information.
On a larger scale, the generative power of AI methods and synthetic media have important implications for defense and national security. The methods can be used by adversaries to generate believable statements from world leaders and commanders, to fabricate persuasive false-flag operations, and to generate fake news events. A recent demonstration includes the multiple examples of manipulated and more sophisticated deepfakes that have come to the fore over the course of the Russian attack on Ukraine. This includes a video of President Volodymyr Zelenskyy appearing to call for surrender.[76]
The proliferation of synthetic media has had another concerning effect: malevolent actors have labeled real events as “fake,” taking advantage of new forms of deniability coming with the loss of credibility in the deepfake era. Video and photo evidence, such as imagery of atrocities, are being called fake. Known as the “liar’s dividend”, the proliferation of synthetic media emboldens people to claim real media as “fake,” and creates plausible deniability for their actions.[77]
We can expect synthetic media and its deployment to continue grow in sophistication over time, including the persuasive interleaving of deepfakes with unfolding events in the world and real-time synthesis of deepfakes. Real-time generations could be employed to create compelling, interactive imposters (e.g., appearing in teleconferences and guided by a human controller) that appear to have natural head pose, facial expressions, and utterances. Looking further out, we may have to face the challenge of synthetic fabrications of people that can engage autonomously in persuasive real-time conversations over audio and visual channels.
6.2 Direction: Digital Content Provenance
A promising approach to countering the threat of synthetic media can be found in a recent advance, named digital content provenance technology. Digital content provenance leverages cryptography and database technologies to certify the source and history of edits (the provenance) of any digital media. This can provide “glass-to-glass” certification of content, from the photons hitting the light-sensitive surfaces of cameras to the light emitted from the pixels of displays, for secure workloads. We pursued an early vision and technical methods for enabling end-to-end tamper-proof certification of media provenance in a cross-team effort at Microsoft.[78],[79] The aspirational project was motivated by our assessment that, in the long-term, neither humans nor AI methods would be able to reliably distinguish fact from AI-generated fictions—and that we must prepare with urgency for the expected trajectory of increasingly realistic and persuasive deepfakes.
After taking the vision to reality with technical details and the implementation of prototype technologies for certifying the provenance of audiovisual content, we worked to build and contribute to cross-industry partnerships, including Project Origin, the Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI), and the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), a multistakeholder coalition of industry and civil society organizations. [80],[81],[82],[83] In January 2022, C2PA released a specification of a standard that enables the interoperability of digital content provenance systems.[84],[85] Commercial production tools are now becoming available in accordance with the C2PA standard that enable authors and broadcasters to assure viewers about the originating source and history of edits to photo and audiovisual media.
The final report of the NSCAI recommends that digital content provenance technologies should be pursued to mitigate the rising challenge of synthetic media. In Congress, the bipartisan Deepfake Task Force Act (S. 2559) proposes the establishment of the National Deepfake and Digital Provenance Task Force.[86] Microsoft and its media provenance collaborators encourage Congress to move forward with standing-up a task force to help identify and address the challenges of synthetic media and we would welcome the opportunity to provide assistance and input into the work.
Recommendations: Defend against malign information operations
Summary
I have covered in my testimony status, trends, examples, and directions ahead with rising opportunities and challenges at the intersection of AI and cybersecurity. AI technologies will continue to be critically important for enhancing cybersecurity in military and civilian applications. AI methods are already qualitatively changing the game in cyber defense. Technical advances in AI have helped in numerous ways, spanning our core abilities to prevent, detect, and respond to attacks—including attacks that have never been seen before. AI innovations are amplifying and extending the capabilities of security teams across the country.
On the other side, state and non-state actors are beginning to leverage AI in numerous ways. They will draw new powers from fast-paced advances in AI and will continue to add new tools to their armamentarium. We need to double down with our attention and investments on threats and opportunities at the convergence of AI and cybersecurity. Significant investments in workforce training, monitoring, engineering, and core R&D will be needed to understand, develop, and operationalize defenses for the breadth of risks we can expect with AI-powered cyberattacks. The threats include new kinds of attacks, including those aimed squarely at AI systems. The DoD, federal and state agencies, and the nation need to stay vigilant and stay ahead of malevolent adversaries. This will take more investment and commitment to fundamental research and engineering on AI and cybersecurity, and in building and nurturing our cybersecurity workforce so our teams can be more effective today—and well-prepared for the future.
Thank you for the opportunity to testify. I look forward to answering your questions.
[1] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2021/12/15/the-final-report-on-nobeliums-unprecedented-nation-state-attack/
[2] https://news.microsoft.com/wp-content/uploads/prod/sites/626/2022/02/Cyber-Signals-E-1-218.pdf, page 3
[3] https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/group/m365-defender-research/
[4] 2018-Webroot-Threat-Report_US-ONLINE.pdf
[5] Microsoft Digital Defense Report, October 2021
[6] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2021/05/12/securing-a-new-world-of-hybrid-work-what-to-know-and-what-to-do/
[7] J. McCarthy, J., M.L. Minsky, N. Rochester, N., C.E. Shannon, C.E. A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Project on Artificial Intelligence, Dartmouth University, May 1955. http://www-formal.stanford.edu/jmc/history/dartmouth/dartmouth.html
[8] https://www.bls.gov/ooh/computer-and-information-technology/information-security-analysts.htm
[9] https://www.isc2.org/News-and-Events/Press-Room/Posts/2021/10/26/ISC2-Cybersecurity-Workforce-Study-Sheds-New-Light-on-Global-Talent-Demand
[10] https://newsroom.trendmicro.com/2021-05-25-70-Of-SOC-Teams-Emotionally-Overwhelmed-By-Security-Alert-Volume
[11] https://www.av-test.org/en/statistics/malware/
[12] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2021/07/27/combing-through-the-fuzz-using-fuzzy-hashing-and-deep-learning-to-counter-malware-detection-evasion-techniques
[13] https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/urltran-improving-phishing-url-detection-using-transformers/
[14] https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3471621.3471858
[15] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2020/07/23/seeing-the-big-picture-deep-learning-based-fusion-of-behavior-signals-for-threat-detection/
[16] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2020/08/27/stopping-active-directory-attacks-and-other-post-exploitation-behavior-with-amsi-and-machine-learning/
[17] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2019/12/18/data-science-for-cybersecurity-a-probabilistic-time-series-model-for-detecting-rdp-inbound-brute-force-attacks/
[18] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2020/06/10/the-science-behind-microsoft-threat-protection-attack-modeling-for-finding-and-stopping-evasive-ransomware/
[19] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2021/12/02/structured-threat-hunting-one-way-microsoft-threat-experts-prioritizes-customer-defense/
[20] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2020/07/09/inside-microsoft-threat-protection-correlating-and-consolidating-attacks-into-incidents/
[21] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2020/07/29/inside-microsoft-threat-protection-solving-cross-domain-security-incidents-through-the-power-of-correlation-analytics/
[22] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2022/02/03/cyber-signals-defending-against-cyber-threats-with-the-latest-research-insights-and-trends/
[23] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2021/05/12/securing-a-new-world-of-hybrid-work-what-to-know-and-what-to-do/
[24] https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2021/04/01/automating-threat-actor-tracking-understanding-attacker-behavior-for-intelligence-and-contextual-alerting/
[25] https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3448016.3452745
[26] Cybersecurity Incidents (opm.gov)
[27] Russian Interference in 2016 U.S. Elections – FBI
[28] Characterizing networks of propaganda on twitter: a case study
[29] https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.15764.pdf
[30] B. Buchanan, J. Bansemer, D. Cary, et al., Automating Cyber Attacks: Hype and Reality, Center for Security and Emerging Technology, November 2020. https://cset.georgetown.edu/wp-content/uploads/CSET-Automating-Cyber-Attacks.pdf
[31] How cyberattacks are changing according to new Microsoft Digital Defense Report
[32] Intelligence, FireEye Threat. “HAMMERTOSS: Stealthy tactics define a Russian cyber threat group.” FireEye, Milpitas, CA (2015).
[33] Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion, Technique T1497 – Enterprise | MITRE ATT&CK®
[34] https://www.jmir.org/2021/5/e26933/
[35] See for example, see documentation of Deep Exploit, tools and demonstration showing the use of reinforcement learning to drive cyberattacks: https://github.com/13o-bbr-bbq/machine_learning_security/tree/master/DeepExploit
[36] https://www.defcon.org/
[37] J. Seymour and P. Tully, Generative Models for Spear Phishing Posts on Social Media, 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05196
[38] https://www.wired.com/story/ai-phishing-emails/amp
[39] Implications of Artificial Intelligence for Cybersecurity: A Workshop, National Academy of Sciences, 2019. https://www.nationalacademies.org/our-work/implications-of-artificial-intelligence-for-cybersecurity-a-workshop
[40] Hey, My Malware Knows Physics! Attacking PLCs with Physical Model Aware Rootkit – NDSS Symposium (ndss-symposium.org)
[41] B. Hitaj, P. Gasti, G. Ateniese, F. Perez-Cruz, PassGAN: A Deep Learning Approach for Password Guessing, NeurIPS 2018 Workshop on Security in Machine Learning (SecML’18), December 2018. https://github.com/secml2018/secml2018.github.io/raw/master/PASSGAN_SECML2018.pdf
[42] S. Datta, DeepObfusCode: Source Code Obfuscation through Sequence-to-Sequence Networks In: Arai, K. (eds) Intelligent Computing. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 284. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-80126-7_45, July 2021.
[43] J. Li, L. Zhou, H. Li, L. Yan and H. Zhu, “Dynamic Traffic Feature Camouflaging via Generative Adversarial Networks,” 2019 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), 2019, pp. 268-276, doi: 10.1109/CNS.2019.8802772. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8802772
[44] C. Novo, R. Morla, Flow-Based Detection and Proxy-Based Evasion of Encrypted Malware C2 Traffic, Proceedings of the 13th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security 2020, https://doi.org/10.1145/3411508.3421379.
[45] D. Han et al., “Evaluating and Improving Adversarial Robustness of Machine Learning-Based Network Intrusion Detectors,” in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 39, no. 8, pp. 2632-2647, Aug. 2021, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9448103
[46] A botnet-based command and control approach relying on swarm intelligence – ScienceDirect
[47] https://www.darpa.mil/program/cyber-grand-challenge
[48] R. Rivest, Chaffing and Winnowing: Confidentiality Without Encryption,” CryptoBytes, 4(1):12-17, https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/aaf3/7e0afa43f5b6168074dae 2bc0e695a9d1d1b.pdf
[49] https://www.nscai.gov/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Full-Report-Digital-1.pdf. page 279.
[50] https://www.cvedetails.com/product/53738/Google-Tensorflow.html
[51] Xiao, Qixue, et al. “Security risks in deep learning implementations.” 2018 IEEE Security and privacy workshops (SPW). IEEE, 2018.
[52] Gu, Tianyu, Brendan Dolan-Gavitt, and Siddharth Garg. “Badnets: Identifying vulnerabilities in the machine learning model supply chain.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.06733 (2017).
[53] Jagielski, Matthew, et al. “Manipulating machine learning: Poisoning attacks and countermeasures for regression learning.” 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). IEEE, 2018.
[54] Yu, Honggang, et al. “CloudLeak: Large-Scale Deep Learning Models Stealing Through Adversarial Examples.” NDSS. 2020.
[55] Ziqi Yang, Ee-Chien Chang, Zhenkai Liang, Adversarial Neural Network Inversion via Auxiliary Knowledge Alignment, 2019
[56] https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/06/22/technology/xinjiang-uyghurs-china-propaganda.html
[57] https://skylightcyber.com/2019/07/18/cylance-i-kill-you/
[58] Finlayson, Samuel G., et al. “Adversarial attacks on medical machine learning.” Science 363.6433 (2019): 1287-1289.
[59] I.J. Goodfellow, J. Shlens, C. Szegedy, Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples, ICLR 2015. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6572.pdf
[60]N. Papernot, P. McDaniel, I. Goodfellow, et al., Practical Black-Box Attacks against Machine Learning, ASIA CCS ’17, April 2017. https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3052973.3053009
[61] M. Alzantot, B. Balaji, M. Srivastava, Did you hear that? Adversarial Examples Against Automatic Speech Recognition, Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 2017. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.00554.pdf
[62] https://www.nscai.gov/
[63] “Upholding Democratic Values: Privacy, Civil Liberties, and Civil Rights in Uses of AI for National Security,” Chapter 8, Report of the National Security Commission on AI, March 2021. https://reports.nscai.gov/final-report/chapter-8/
[64] “Establishing Justified Confidence in AI Systems,” Chapter 8, Report of the National Security Commission on AI, March 2021. https://reports.nscai.gov/final-report/chapter-7/
[65] E. Horvitz J. Young, R.G. Elluru, C. Howell, Key Considerations for the Responsible Development and Fielding of Artificial Intelligence, National Security Commission on AI, April 2021. https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2108/2108.12289.pdf
[66]Kumar, Ram Shankar Siva, et al. Adversarial machine learning-industry perspectives. 2020 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW). IEEE, 2020.
[67] https://cacm.acm.org/magazines/2018/7/229030-making-machine-learning-robust-against-adversarial-inputs/fulltext
[68] A. Madry, A. Makelov, L. Schmidt, et al. Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks, ICLR 2018. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.06083.pdf
[69] https://breakingdefense.com/2021/11/china-invests-in-artificial-intelligence-to-counter-us-joint-warfighting-concept-records/
[70] https://atlas.mitre.org/
[71] https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/security/engineering/failure-modes-in-machine-learning
[72] https://github.com/Azure/counterfit/
[73] https://mlsec.io/
[74] https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/2091996/dod-adopts-ethical-principles-for-artificial-intelligence/
[75] https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
[76] See: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X17yrEV5sl4
[77] The Liar’s Dividend: The Impact of Deepfakes and Fake News on Politician Support and Trust in Media | GVU Center (gatech.edu)
[78] P. England, H.S. Malvar, E. Horvitz, et al. AMP: Authentication of Media via Provenance, ACM Multimedia Systems 2021. https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3458305.3459599
[79]E. Horvitz, A promising step forward on disinformation, Microsoft on the Issues, February 2021. https://blogs.microsoft.com/on-the-issues/2021/02/22/deepfakes-disinformation-c2pa-origin-cai/
[80] Project Origin, https://www.originproject.info/about
[81] J. Aythora, et al. Multi-stakeholder Media Provenance Management to Counter Synthetic Media Risks in News Publishing, International Broadcasting Convention 2020 (IBC 2020), Amsterdam, NL 2020 https://www.ibc.org/download?ac=14528
[82] Content Authenticity Initiative, https://contentauthenticity.org/
[83] Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), https://c2pa.org/
[84]C2PA Releases Specification of World’s First Industry Standard for Content Provenance, Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity, January 26, 2022, https://c2pa.org/post/release_1_pr/
[85] https://erichorvitz.com/A_Milestone_Reached_Content_Provenance.htm
[86] Deepfake Task Force Act, S. 2559, 117th Congress, https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/senate-bill/2559/text
Tags: artificial intelligence, cyberattacks, department of defence, US government
Have the latest posts sent right to your inbox. Enter your email below.
By providing your email address, you will receive email updates from the Microsoft on the Issues blog.
Follow us:
- Published in Uncategorized
Microsoft 365 launches new Records Management Solution – IDM.net.au
Microsoft has announced the general availability of Records Management in Microsoft 365 (formerly known as Office365) for “Eligible Microsoft 365 E5 customers”, a new tool to help businesses protect and manage sensitive data. E5 is the top tier and highest priced enterprise level of Microsoft 365
While all Microsoft 365 users will see the Records management tool in the Microsoft 365 compliance center, this will change according to release notes.
“At this time any customer will be able to see the solution even if you’re not licensed for it, although not all functionality will work as expected. In the near future, this will change, and you won’t be able to see records management options if you’re not appropriately licensed.”
The new Records Management solution differs from SharePoint’s in-place records management or records center.
“This solution is our next evolution in providing Microsoft 365 customers with records management scenarios. It uses a different underlying technology than our legacy functionality in SharePoint, and also goes across Microsoft 365 beyond just SharePoint. This new solution is where our future investments in records management will be made and we recommend any SharePoint Online customers using SharePoint’s in-place records management, content organizer, or the SharePoint records center to evaluate migrating to this new way of managing your records,” Microsoft states.
The new tool promises the ability to:
A new Harvard Business Review research report, commissioned by Microsoft, found 77% of organizations believe an effective security, risk, and compliance strategy is essential, but 61% face challenges in creating one. More than half (53%) have not developed a strong, business-wide data governance approach. The majority (82%) say protecting information has grown increasingly difficult due to new risks and complexities brought on by digital transformation.
“With many employees working remotely right now, one of the things we hear is security and risk management are arguably more important than ever,” says Alym Rayani, senior director at Microsoft 365. The HBR survey was conducted before the coronavirus pandemic, he notes, but its data is just as important at a time when businesses are relying on remote employees.
A higher volume of information, transmitted through and stored in multiple collaboration systems, drives complexity for managing records with cost and risk implications. Companies facing increasing regulations often move data into different systems of record to comply. This can increase the risk of missing records or not properly declaring them, he says in a blog post.
The records-management solution supports the following elements:
According to one local records management expert, there may be some challenges in adapting the solution for conditions in Australia and New Zealand.
“The design will be based on the US vision for records management – i.e. applying a file plan classification (label) to a records in place, and not place the records in context. The UK/AUS approach to records management is to collect the records together so it makes up a story – i.e. the evidence of a business transaction is clearly understood because you can see the context of the story. The US method usually leaves the document/record where it is, which makes it hard to find in the Office 365 information maze.
“As an example, one Australian Federal Government department tried many years ago to re-configure an American document management system to manage records by collecting the records into a file to ensure they showed context. But it broke the system and it was eventually recommended that the system be replaced.”
Office 365 and SharePoint specialist Andrew Warland, who blogs at andrewwarland.wordpress.com, notes that the concept of ‘declaring’ a record is an American concept that isn’t used here.
“I’m very familiar with the information governance aspects of Microsoft Office 365 and have been critical of some of the things like auto-classification (for E5 only) as, while it is well-intentioned and would probably work well for some organisations, there are some potential risks in doing things this way as opposed to a good combination of retention policies applied to the different workloads across the environment,” said Warland.
“What I am not clear about, yet, is the extent to which some of these functions will be limited to E5 customers or will remain with the more common E3 licence. For example, the creation of ‘explicit’ retention labels (published as retention policies) or ‘implicit’ (invisible to users) retention policies, which can be applied to almost all of the ecosystem, are still visible in my E3 tenant. I’ve seen some people say that these will be removed, only accessible by E3 licence holders, but I’m not sure about that. Certainly, other features such as auto-classification, or more granular event-based policies, may require the E5 licence.
“When it comes to auto-classification I am curious why Microsoft made this sound like new technology. Products like Recommind (now owned by Open Text) have been doing that for close to 20 years.
“I agree with Microsoft that there is now so much digital content you cannot realistically expect to manage retention manually. However, the ability to create and apply both ‘implicit’ and ‘explicit’ (label based) policies cover almost all the content fairly well. I’m not sure what value things like auto-classification brings to the market and I’m a bit sceptical with the use cases suggested for event-based retention policies – for example, things like contract expiry dates or the date when employees leave an organisation can both be impacted by factors out of an organisation’s control (litigation, investigations). I wouldn’t want to see critical records vanish without a trace in this way.”
- Published in Uncategorized









